1 principle and purpose
The LED light source is a low-voltage DC device. Therefore, the LED lamp needs to have a power supply capable of converting 220 V AC into a low-voltage DC that meets the LED operation requirements, but the stage and film lamps need to have a dimming function, so the power supply thereof More complicated. At present, the mainstream mode of the power supply device configured with LED lamps in the studio is:
(1) The pre-stage uses a common pulse width modulation (PWM) switching power supply, as a low-voltage DC power supply, the switching frequency is usually several tens of kilohertz.
(2) The latter stage performs the low-frequency pulse width modulation in a chopping manner, and adjusts the duty ratio to adjust the brightness of the lamp. This part of the circuit is usually developed by the luminaire factory, and the switching frequency varies greatly from factory to factory. Usually ranging from hundreds of Hertz to tens of kilohertz.
In the pulse width modulation mode of operation, the power device's chopping of the current produces higher harmonics, which cause radio disturbances to audio and video systems and other weak systems in theaters and studios, which may affect the normal operation of other devices. . In addition, since the rectifier circuit and the capacitor filter circuit in the power supply device distorted the power frequency current, the generated low-order harmonics may cause pollution to the power grid and affect the operation of other electrical equipment.
Therefore, a series of tests are required for LED luminaires: testing according to GB 17743-2007 "Limitations and Measurement Methods for Radio Disturbance Characteristics of Electrical Lighting and Similar Equipment", and measuring whether the radio disturbance characteristics meet the requirements of the standard; According to the national standard GB 17625.1-2003 "electromagnetic compatibility limit harmonic current emission limit (equipment input current per phase ≤ 16A)" test, test whether its harmonic current meets the requirements of the standard.
Through the experiments and research of this subject, we can understand the relevant data of electromagnetic interference that LED lamps can produce in the studio, and propose corresponding solutions.
2 experimental content and method
2.1 Experimental conditions
This research requires a variety of professional electromagnetic compatibility test equipment, such as power analyzers, artificial power networks, conducted test receivers, radiated interference receivers and three-ring antennas. Some tests also need to be carried out in anechoic chambers. Therefore, it is necessary. Entrusted by professional testing agencies approved by relevant state departments for testing.
2.2 Test lamps
There are 2 types and 5 models for the test lamps. 1 luminaire for each model, a total of 5 luminaires. See 1.
2.3 Experimental content
(1) According to the requirements of GB 17743-2007, find the maximum disturbance point generated during the dimming process and measure the radio disturbance value at that point.
(2) According to the requirements of national standard GB 17625.1-2003, the luminaire is divided into five equal stages between the minimum power and the maximum power, and the harmonic components of each stage are tested.
2.4 Experimental methods and procedures
The luminaire to be tested is aged for 100 hours, and then the parameters of the luminaire are stabilized before being sent for inspection.
2.4.1 Radio disturbance test
2.4.1.1 Conducted disturbance voltage test
Tested at the power supply end and control end of the lamp according to the requirements of GB 17743-2007.
(1) The lamp power terminal test is carried out in the following five frequency bands: 9 kHz to 50 kHz; 50 kHz to 150 kHz; 150 kHz to 0.5 MHz; 0.5 MHz to 5.0 MHz; 5.0 MHz to 30 MHz.
(2) The control end of the luminaire is tested in the following two frequency bands: 150 kHz to 0.5 MHz; 0.5 MHz to 30 MHz.
2.4.1.2 Radiated electromagnetic disturbance test.
Tested according to the requirements of national standard GB 17743-2007.
(1) The frequency range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz is tested in the following four frequency bands: 9 kHz to 70 kHz; 70 kHz to 150 kHz; 150 kHz to 3.0 MHz; 3.0 MHz to 30 MHz.
(2) In the anechoic chamber, the frequency range of 30 MHz to 300 MHz is tested in the following two frequency bands: 30 MHz to 230 MHz; 230 MHz to 300 MHz. 2 is the electromagnetic interference test device in the frequency range of 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Schematic.
The limits of radio disturbance characteristics of the above tests are given in GB 17743-2007.
2.4.2 Harmonic testing
According to the national standard GB 17625.1-2003 for the requirements of Class C equipment and built-in dimmer luminaires, the harmonic components of the luminaire are tested and divided into five equal stages between the minimum power and the maximum power, ie at 20%, 40%. The harmonic components are tested under 60%, 80% and 100% power conditions. The range of the harmonic order n is: n = 2, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11 ≤ n ≤ 39 (only odd harmonics) Wave) 3 is a schematic diagram of the harmonic current test device.
The harmonic current emission limits of the above tests are shown in GB 17625.1-2003.
3 experimental results and analysis
From the luminaire samples 1 to 5 of this study, 1, 3 and 4 lamps were selected and sent to the Beijing Household Appliance Quality Supervision and Inspection Station for testing, but the test results of each luminaire exceeded the limits specified by the standards to varying degrees. The luminaire factory has made technical improvements to the luminaires, and the improved 1 luminaires have been re-inspected and passed two standard tests.
The 5 and 2 lamps were sent to relevant testing institutions in Guangzhou for testing, and they have passed two standard tests.
The following is an analysis of the main test parameters of three of the lamps.
3.1 1 luminaire test results
3.1.1 Measurement of radio disturbance characteristics
(1) Conducted disturbance voltage test
A. The power supply terminal frequency of the luminaire is the conduction disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz. Participation.
B. The power supply terminal frequency of the luminaire is the conduction disturbance voltage (average value) in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz. Participation.
(2) Radiated electromagnetic disturbance test
A. Radiated electromagnetic disturbance in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz. According to GB 17743-2007, the luminaire should be tested in three mutually orthogonal loop antenna systems. Each loop antenna is tested for radiated electromagnetic disturbance, 6 is the horizontal ring. The radiated electromagnetic disturbance value of the antenna test.
B. Radiated electromagnetic disturbance in the frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. This test is tested by CDN method. The limit should meet the corresponding requirements of GB 17743-2007. The test results are shown in 7.
4 Conduction disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz at the power supply terminal Note: The red dotted line is the quasi-peak value of the disturbance voltage, and the purple dotted line is the average value of the disturbance voltage. Note: The red dotted line is the quasi-peak limit value of the disturbance voltage, and the purple dotted line is the average value of the disturbance voltage.
The above test is based on the test unit to indicate that it is about 42% of full power (control data is hexadecimal 6C, maximum value is FF), and the test data when the radio disturbance is maximum. According to the above test data, the conduction disturbance voltage and radiated electromagnetic disturbance of the power supply end of the 1 lamp meet the requirements of GB 17743-2007.
Note: This test did not test the conduction disturbance voltage of the control terminal.
3.1.2 Harmonic current measurement
According to the requirements of GB 17625.1-2003, it should be divided into five equal stages between the minimum power and the maximum power, that is, the harmonic components are tested under the conditions of 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% power. The test unit only provides 20% of the test data when the interference is greatest in other cases.
(1) When the full power is 20%, that is, 24 W or so, the test data is 8.
(2) Except for 20% of full power, the test data when the harmonics of other powers are maximum is shown in 9.
According to the above test data, the harmonic current of 1 luminaire meets the requirements of GB 17625.1-2003. At low power (20%), although there are large even harmonics, GB 17625.1-2003 has even times other than 2 times. Harmonics are not limited.
This is also the cause of the large distortion of the current waveform (0), which should be taken seriously.
3.2 5 luminaire test results
3.2.1 Measurement of radio disturbance characteristics
(1) Conducted disturbance voltage test
A. The power supply terminal frequency of the luminaire is the conduction disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz, see 11.
B. The control terminal frequency of the luminaire is the conducted disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) in the range of 150 kHz to 30 MHz. See 12.
(2) Radiated electromagnetic disturbance test
A. The luminaire radiates electromagnetic disturbances in the frequency range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz.
According to GB 17743-2007, the luminaire should be tested in three mutually orthogonal loop antenna systems, each measuring the radiated electromagnetic disturbance, and 13 is the radiated electromagnetic disturbance value of one of the loop antenna tests.
7 Radiated electromagnetic disturbances tested by the CDN method in the range of 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Note: The red dotted line is the radiated electromagnetic disturbance limit.
Note: The blue line in the figure is the 100% limit and the red line is the 150% limit.
8 Harmonic current at 20% of full power Note: The blue line in the figure is the 100% limit and the red line is the 150% limit.
Note: The blue line in the figure is the lamp current, and the green line is the power supply voltage.
10 1 The current waveform of the luminaire is 20% of the total power, and the harmonic current of the other harmonics of the other powers is 12. The frequency of the control terminal is 150 kHz to 30 MHz. The conduction disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) B. The electromagnetic interference is radiated in the frequency range of 30 MHz to 300 MHz.
Due to the small anechoic chamber, it is not possible to test at a distance of 10 m according to the test requirements of GB 17743-2007. The actual test distance for radiated electromagnetic disturbance in the frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz is 3 m, according to the national standard GB 9254-2008. 10.8 of the Radio Disturbance Limits and Measurement Methods for Information Technology Equipment, if tested at different test distances, may be converted according to the following formula:
L 2 = L 1 (d 1 / d 2) L 1 - the limit value L 2 at the distance d 1 - the new limit value at the distance d 2 Therefore, the limit value of GB 17743-2007 is converted into. The test results of the vertical direction and horizontal direction of the antenna are shown in 4.
The above test is carried out according to the detection unit at full power, and the full power is the maximum state of radio harassment of the lamp. According to the above test data, the conduction disturbance voltage and the radiated electromagnetic disturbance of the power supply and control terminals of the 5 lamps meet the requirements of the national standard GB 17743-2007. The testing unit provides a formal test report for the lamp test.
Note: The upper red line is the quasi-peak limit value of the disturbance voltage, and the lower red line is the average value of the disturbance voltage.
11 Lamp power terminal frequency is 9 kHz ~ 30 MHz range of conducted disturbance voltage (quasi-peak) Note: Red line is the radiation electromagnetic disturbance limit.
Note: The upper red line is the quasi-peak limit value of the disturbance voltage, and the lower red line is the average value of the disturbance voltage.
13 Frequency in the range of 9 kHz to 30 MHz Radiated electromagnetic disturbance frequency range / MHz quasi-peak limit dB (μV / m) 30 ~ 230 40 230 ~ 300 47 Note: Red line is the radiated electromagnetic disturbance limit, see 2 for the limit .
14 Frequency radiated electromagnetic interference in the range of 30 MHz to 300 MHz Note: There is a different view on the accuracy of the test method for reducing the test distance and limit conversion. Generally, the CDN test method can be used when the anechoic chamber cannot meet the test distance of 10 m. This test method is permitted by GB 17743-2007.
2 reduce the test distance limit conversion results
3.2.2 Harmonic current measurement
According to the requirements of GB 17625.1-2003, it should be divided into five equal stages between the minimum power and the maximum power, that is, the harmonic components are tested under the conditions of 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% power. The following are the test data in 5 cases, see 15~19.
According to the above test data, the harmonic currents of the five lamps all meet the requirements of GB 17625.1-2003. In the five power test processes, the 11th harmonics are relatively injected. In the figure, the blue line is the lamp current and the green line is the power supply voltage.
Note: The blue line in the figure is the 100% limit, the red line is the 150% limit, and the limit is referred to Appendix B.
Larger, but below the limit. And the lamp current waveform distortion is relatively small. See 20.
3.3 3 luminaire test results
The lamp was tested for harmonics at full power (50 W) and the results were as follows.
It can be seen that most of the harmonic currents exceed the provisions of GB 17625.1-2003, and the “Fail†in the table indicates failure. In addition, the lamp has a particularly low power factor of only 0.455.
Note: This lamp is only tested under full power. It is not divided into 5 equal stages between minimum power and maximum power according to the requirements of GB 17625.1-2003, ie not at 20%, 40%, 60%, 80. Each harmonic component is tested under % and 100% power conditions.
4 conclusions and recommendations
4.1 Conclusion
LED luminaires will generate a certain degree of radio harassment and harmonics when working, but as long as the electromagnetic compatibility of high-quality power supply devices is installed in the luminaire, electromagnetic interference can be controlled within the scope of the standard license, and the luminaires that meet the relevant standards will not affect the studio. And the normal work of other equipment on the stage.
4.2 Suggestions
(1) The standards for electromagnetic compatibility are mandatory standards. When purchasing LED lamps, they should be strictly controlled in terms of electromagnetic interference. Suppliers should be required to provide test reports of relevant standards.
(2) Even if the LED lamp that meets the relevant standards works, it will produce a certain degree of 3rd harmonic. Although the absolute value is not too large, it should be paid attention to when using LED lamps in large quantities. Harmonic test data shows that the current waveform of the LED lamp will be distorted to varying degrees. In the three-phase power supply, the third harmonics in each phase line cannot cancel each other out in the neutral line of the power supply. Therefore, the cross-sectional area of ​​the neutral line of the studio lighting power supply line should not be too small. The line cross-sectional area is equivalent.
(3) In this study, the test items and methods were different because the lamps were commissioned by different test units. If some luminaires do not test the radio disturbance value on the control end, in the harmonic test, some luminaires are not tested in 5 equal stages. As a new type of luminaire, LED performance luminaires are not very clear in the relevant national standards. It is recommended that relevant standards be formulated as soon as possible to clarify the quality requirements for electromagnetic interference.
JoyLED Indoor LED Module including full color LED Module, single color and double color LED modules, SMD module etc. All JoyLED indoor modules were strictly tested before shipment. You can get the best price Led Module with CE,RoHs,FCC approved.
JoyLED indoor LED Modules include the models of: P1.25mm, P1.562mm, P1.875mm, P1.667mm, P1.923mm, P2.0mm, P2.5mm, P3mm, P3.91mm, P4mm, P4.81mm, P5mm, P6mm, P6.25mm, P7.62mm, P10mm.
Nowadays, more and more customer need higher resolution to improve the video quality, so indoor UHD series of P1.25mm, P1.562mm, P1.875mm, P1.667mm, P1.923mm, P2.0mm, P2.5mm, P3mm, P3.91mm, P4mm is the most common used models. JoyLED Indoor Led Module is widely used for Advertising media, monitoring center,command center, energy center, education center, television station, radio station, conference center, transportation, real estate, sports venues, leasing, stage performing arts, studio etc.
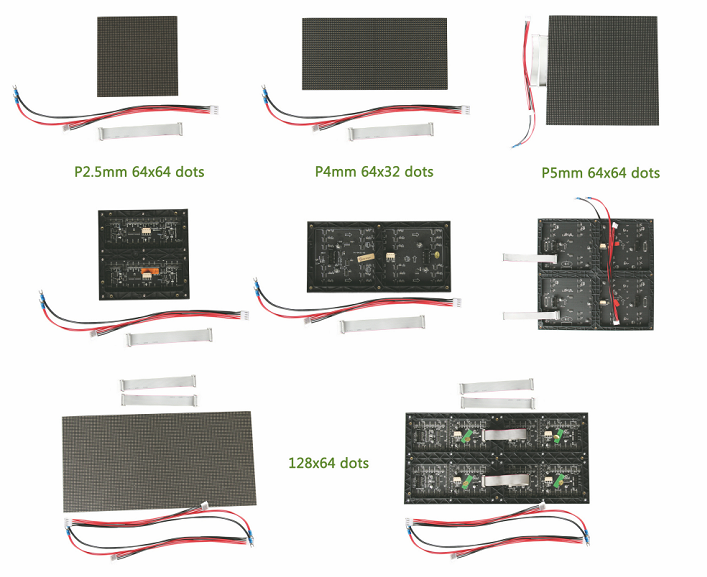
Indoor LED Module
Indoor Led Module,P3 Flexible Led Module,Indoor Led Display Module,Advertising Board Led Module
Shenzhen Joy LED Display Co., Ltd. , https://www.joe-led.com