The guidance of the AGV refers to calculating the actual control command value of the AGV according to the position information provided by the AGV steering sensor, that is, giving the set speed and steering angle of the AGV, which is the AGV control. The key to technology. In short, AGV's guidance control is AGV trajectory tracking. There are several ways to guide the AGV. For example, using the center point of the guiding sensor as a reference point, tracking the virtual point on the guiding magnetic strip is one of them. The control target of the AGV is to correct the rotational speed of the driving wheel to change the traveling direction of the AGV by detecting the relative position of the reference point and the virtual point, and try to make the reference point above the virtual point. This way the AGV can always track the boot line.
After receiving the material handling instruction, the controller system calculates, plans and analyzes according to the stored running map and the current position and driving direction of the AGV trolley, selects the best driving route, and automatically controls the driving and steering of the AGV trolley when the AGV is used. After reaching the loading position and accurately parking the position, the transfer mechanism moves to complete the loading process. Then the AGV car starts and drives to the target unloading point. After the accurate parking, the transfer mechanism acts, completes the unloading process, and reports its position and status to the control system. The AGV car then starts and heads for the standby area. Wait until the new order is received before making the next move.

1. High degree of automation;
Controlled by computer, electronic control equipment, magnetic induction SENSOR, laser reflector.
When a certain part of the workshop needs auxiliary materials, the staff inputs relevant information to the computer terminal, and the computer terminal sends the information to the central control room, and the professional technician sends instructions to the computer. Under the cooperation of the electronic control equipment, this The instructions are eventually accepted and executed by the AGV – the excipients are delivered to the appropriate location.
2. Charging automation;
When the power of the AGV car is about to run out, it will send a request command to the system to request charging (the general technician will set a value in advance), and automatically "queue" the charging to the charging place after the system allows it.
In addition, the AGV car has a long battery life (more than 2 years) and can work for about 4 hours per 15 minutes of charging.
3, beautiful, improve the degree of appreciation, thereby improving the image of the company.
4, convenient, reduce the floor space; AGV trolleys in the production workshop can shuttle back and forth in various workshops.
The structural composition of the AGV trolley1, the car body
The physical body of the AGV, the frame and the corresponding mechanical components, are the basis for the installation of other assembly components.
2, drive power unit
AGVs are often powered by 24V and 48V DC batteries. A lead-acid battery or a lithium battery is often used, and the lithium battery can be automatically charged and can work 24 hours.
3, the drive device
The wheel, reducer, brake, drive motor and speed controller are components that control the normal operation of the AGV. The running command is issued by computer or manual control, and the adjustment of running speed, direction and braking is controlled by computer respectively. For safety, the brake can be mechanically braked in the event of a power failure.
4, guiding device
The magnetic permeability sensor + landmark sensor receives the direction information of the guiding system, and realizes the forward, backward, branching, and outbound operations of the AGV through the guiding + landmark sensor.
5, the car controller
Accept the instructions of the control center and execute the corresponding instructions, and timely feedback the status (such as position, speed, etc.) to the control center.
6, communication device
Realize the exchange of information between AGV and ground control station and ground monitoring equipment.
7, safety protection device
Obstacle sensor + physical anti-collision (black pegs under the sensor) + emergency stop switch, mainly for the protection of people, AGV itself or other equipment.
8, the carrier
Traction bar: A device that directly contacts the goods being transported to carry cargo.
9. Information transmission and processing device
The AGV is monitored, the ground state of the AGV is monitored, and information is transmitted in real time with the ground control station.

The so-called AGV guidance method refers to the way to determine the direction and path of its operation. It is different from the general communication mentioned above. The commonly used guiding methods are divided into two categories: the predetermined path mode and the unscheduled path mode.
(1) The external route guidance method refers to the provision of information media for guidance on the path of travel. The AGV obtains guidance by guiding its information, such as electromagnetic guidance, optical guidance, and tape. Guidance (also known as magnetic guidance).
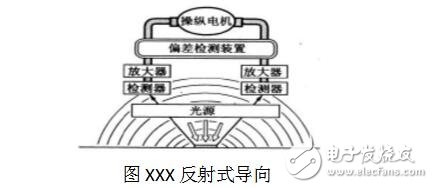
Reflective tape or tape guide1) Reflective guidance. As shown in Figure XXX, this guiding method is to continuously lay a belt made of luminescent material on the ground, or apply it on the specified running route with luminescent paint, and install a reflective light sensor at the bottom of the vehicle. The device drives the steering motor to constantly adjust the direction in which the vehicle is heading.
2) Magnetic guidance. A metal magnetic tape is continuously laid on the ground, and a magnetic sensor is mounted on the vehicle to detect the magnetic field of the magnetic tape, and the steering motor is driven to adjust the driving direction of the vehicle by the magnetic field deviation measurement control.
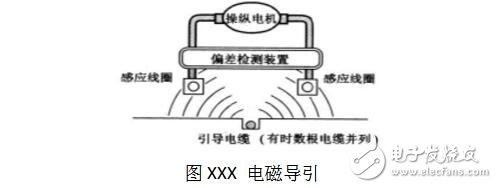
Electromagnetic induction guidanceElectromagnetic induction guidance is currently the most widely used guidance method for AGV (see Figure XXX). It is generally necessary to bury the cable in the ground slot (about 51mm wide, 15mm deep), turn on the low voltage, low frequency signal, and generate a magnetic field around the wire. Two induction coils are installed on the vehicle and are placed on both sides of the guide line. The current in the guide line is about 200 to 300 mA, and the frequency is 2 kHz to 35 kHz. When a high-frequency current flows through the wire, an electromagnetic field is generated around the wire, and two electromagnetic sensors are symmetrically mounted on the AGV, and the difference in the intensity of the electromagnetic signals received by them can reflect the extent to which the AGV deviates from the path. The AGV's automatic control system controls the steering of the vehicle based on this deviation. Continuous dynamic closed-loop control ensures stable and automatic tracking of the set path by the AGV. This electromagnetic induction guided navigation method is currently used on most commercial AGVS, especially for large and medium-sized AGVs.
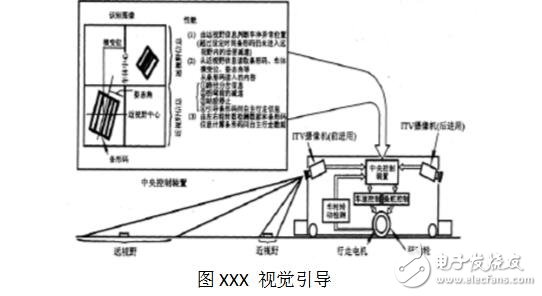
Visual guidance is to intermittently set a number of guiding signs or reflectors (also glass balls) on the path, and the trolley automatically recognizes and judges the path accordingly (see Figure XXX). In addition to the barcode, the guided logo can also be a circle, a square, an arrow, and the like. The vision-guided AGV is an AGV that is rapidly developing and mature. The AGV is equipped with a CCD camera and a sensor, and an image database of the surrounding environment of the AGV travel path is provided in the on-board computer. During AGV driving, the camera dynamically acquires image information of the surrounding environment of the vehicle and compares it with the image database to determine the current location and make decisions for the next step. This method has the best guiding flexibility in theory because it does not require any physical path setting. With the rapid development of computer image acquisition, storage and processing technology, the practicality of this kind of AGV is getting stronger and stronger. In addition, there are various forms of AGV such as ferromagnetic gyro inertial guided AGV and optical guided AGV.
(2) Unscheduled path (free path) guidance mode refers to the way to store the dimensional coordinates on the layout on the AGV, and to determine the driving path from the main ground by identifying the current orientation of the vehicle body, also known as the onboard software. A programmed path mode; the second refers to laser guidance.
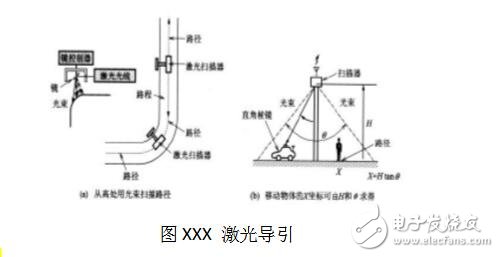
Laser guidanceThe AGV is equipped with a rotatable laser scanner, and a laser positioning mark with a highly reflective reflector is mounted on a wall or pillar along the running path. The AGV relies on a laser scanner to emit a laser beam, and then receives reflection from the surrounding positioning mark. The returned laser beam, the on-board computer calculates the current position of the vehicle and the direction of the movement, and corrects the orientation by comparing with the built-in digital map, thereby realizing automatic handling. At present, the application of this method is more and more common. And according to the same guiding principle, if the laser scanner is replaced with an infrared emitter or an ultrasonic transmitter, the laser-guided AGV can be changed to an infrared guided AGV and an ultrasonic guided AGV.
In order to ensure the accuracy and reliability of positioning, suitable sensors must be used, and different sensors form different positioning methods. There are mainly positioning methods based on photosensitive devices, positioning methods of eddy current sensors, positioning methods of photoelectric sensors, and sensor combination positioning methods.
Photosensor based positioning methodThe principle of this positioning method is the photoelectric effect. It is known from the light-emitting characteristics of the phototransistor that there is a good linearity between the photocurrent output and the illuminance. As the AGV keeps close to the target position, its illuminance increases, and the output of the photosensor increases, thereby controlling the positioning of the AGV. The positioning method has a long effective detection range and can reach more than 200 mm, but the positioning accuracy is low, and the output change of the photosensitive device during the whole positioning process is not obvious, which brings difficulties to the calibration.
Positioning method based on eddy current sensorThe eddy current sensor has a large linear measurement range and high sensitivity, and can directly measure the displacement. This positioning method enables precise positioning. The main component of the eddy current sensor is a coil, and its shape and size are related to the sensitivity and measurement range of the sensor. The detection range is generally long (100 mm or more) during positioning, and thus the volume is large. The electromagnetic field generated when the coil is operated has a magnetic influence on the coordinate guiding method and the sensor used in the electromagnetic induction guiding method.
Photoelectric sensor based methodThis positioning method consists of a photoelectric pair tube. Under normal circumstances, the receiving tube can receive infrared signals. When the AGV reaches the destination, the AGV blocks the infrared light and causes a control signal to be issued. This positioning accuracy can reach more than 1.5mm. If a small light gap is installed in front of the launch tube, the positioning accuracy can be increased to more than 0.6 mm. However, this positioning method cannot control the AGV after the automatic guidance ends until the final precise positioning.
Sensor combination positioning methodThe sensor combination positioning method consists of two parts: light guiding and fine positioning. The light guide is guided by a photosensitive device. Since the effective detection range of the photosensitive device is long, the accuracy is poor, and the precise positioning cannot be performed, and the magnetic sensor has high precision. The combined method can combine the advantages of the two. When positioning, it is guided by infrared rays to make it close to the target position, and finally fine positioning is performed by fine positioning components (such as proximity switches). This method is highly accurate, but the device is more complicated.
Recommended reading:
How does the agv car work? Development status and application field analysis of agv car
How to achieve positioning of agv car
Characteristics and comparative analysis of rgv trolley and agv trolley
Replacement Bulb Lamp With Housing
Replacement Projector Lamp with housing has one more case than the bare bulb lamp, which can be directly put into the projector and more convenient than the installation of the bare bulblamp. The projection effect is the same as the compatible projector lamp, with stable light source and brightness, which can support daily life use
Replacement Bulb Lamp With Housing,Bulb Lamp,Dynamic Projector Lamp,Led Projector Lamp
Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.happybateprojector.com