MAXQ series microcontrollers use JTAG as a debugging and programming tool in system development. For ease of evaluation, we provide a serial port-JTAG adapter. MAXQ microcontrollers can be connected to RS-232 serial ports. Many third-party developers also use this adapter in their integrated development environment (IDE) to connect to MAXQ microcontrollers. Two commonly used IDEs for MAXQ microcontrollers are IAR Embedded Workbench® and CrossWorks from Rowley.
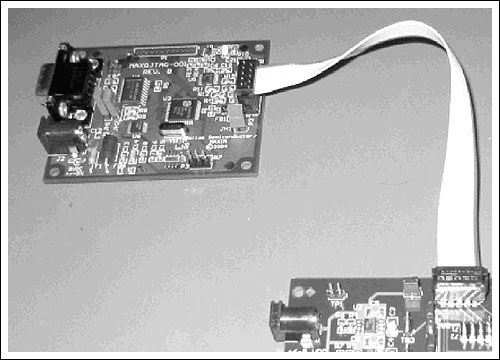
Figure 1. MAXQ serial-JTAG interface board
This JTAG board accepts commands from RS-232, converts the received signal level to TTL level, and finally converts the command to an acceptable JTAG command. These commands should be accepted by any MAXQ microcontroller in the list. The conversion function is actually performed by the DS89C430 on the JTAG board (Note: DS89C420 may be used in earlier models, the instructions in this application note still apply) Ultra-high-speed 8051 microcontroller, DS89C430 built-in flash memory, used to store the conversion firmware. When Maxim releases new firmware or the firmware is damaged for some reason, it needs to be reloaded.
In two cases, the firmware of the JTAG board needs to be updated: Microcontroller Toolbox (MTK), which is download software provided by Maxim to support all 8051 and MAXQ microcontrollers, and the toolbox software can be downloaded. Copy the firmware of the JTAG board, you can get the latest firmware from the latest version of the MAX-IDE software package that supports the MAXQ microcontroller. Although MAX-IDE is not required to install the firmware, the firmware program of the JTAG board is integrated into the installation program of this software, so you must first install this software. After installing MAX-IDE, you can find the JTAG firmware (jtag.hex) in the C: \ Program Files \ MAX-IDE \ Devices \ MAXQ \ JTAGFirmware directory, you can download (ZIP) MAX-IDE. After obtaining the two software, you can update the firmware of the interface board as follows: First, connect the serial port of the PC and the JTAG board with a serial cable, and power on. It must be noted that the JTAG board requires a DC regulated power supply of 5V ± 5%, and also ensure that the connection cable (P2) is disconnected from the JTAG board and the target board before powering on. At power-up, the DS1 LED of the JTAG board should be lit. Confirm that the jumpers JH1 and JH2 on the JTAG board are connected. Start the MTK software and select DS89C430 in the "Select device" interface.
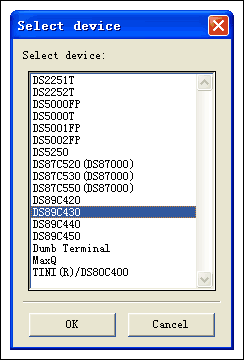
In the "OpTIons" menu, select "Configure Serial Port", and select the corresponding serial port and baud rate, because the internal program loader of DS89C430 uses an automatic way to detect the communication baud rate, and 7.37MHz crystal is used on the board. Therefore, the highest baud rate that can be synchronized with the outside is 38400bps.
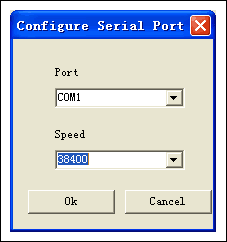
In the "Target" menu, select "Open COMx at 38400 baud" (COMx here is the selected serial port), and then select "Connect to Loader", you should see the following welcome interface: (Note that after connecting to the loader, JTAG DS1 on the board will go out).
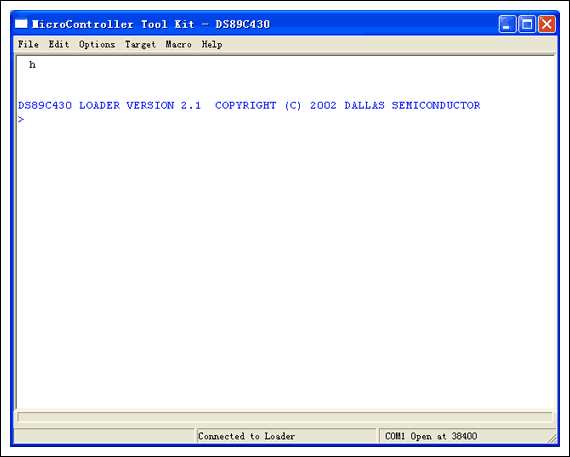
In the "File" menu, select "Load Flash", and then find the folder where the JTAG firmware is located. If you use the firmware in MAX-IDE, you can find it in the directory C: \ Program Files \ MAX-IDE \ Devices \ MaxQ \ JTAGFirmware The firmware.
Select this jtag.hex and open it, MTK will automatically start downloading firmware to the DS89C430 microcontroller on the JTAG board, and give the following prompt when the download is complete.
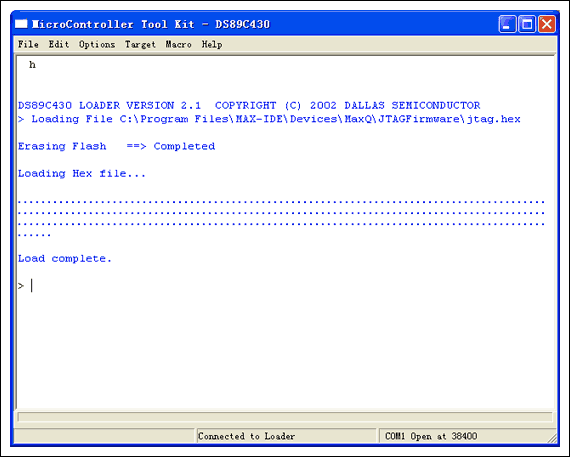 Select "Close COMx" in the "Target" menu to close the serial port, and the DS1 of the JTAG board will light up again. After the above steps are completed, the firmware update of the serial-JTAG interface board is completed.
Select "Close COMx" in the "Target" menu to close the serial port, and the DS1 of the JTAG board will light up again. After the above steps are completed, the firmware update of the serial-JTAG interface board is completed.
What is Car Ethernet
Car Ethernet is a new local area network technology that uses Ethernet to connect the electronic unit in the car. Unlike traditional Ethernet, which uses 4 unshielded twisted pair cables, car Ethernet can achieve a transmission rate of 100Mbit/s or even 1Gbit/s on a single pair of unshielded twisted pair cables. At the same time, it also meets the requirements of the automotive industry for high reliability, low electromagnetic radiation, low power consumption, bandwidth allocation, low latency and synchronous real-time. The physical layer of on-board Ethernet uses BroadRReach technology, and BroadR-Reach's physical layer (PHY) technology has been standardized by the One-pair Ethernet Alliance (OPEN). Therefore, it is sometimes called Broad RReach (BRR) or OABR (Open Alliance BroadR-Reach). The MAC layer of vehicle Ethernet adopts the IEEE 802.3 interface standard and seamlessly supports widely used high-level network protocols (such as TCP/IP) without any adaptation.
On-board Ethernet protocol architecture
Vehicle-borne Ethernet and its supported upper-layer protocol architecture are shown in Figure 1. Vehicle-borne Ethernet mainly involves OSI layer 1 and Layer 2 technologies, while vehicle-borne Ethernet also supports AVB, TCP/IP, DOIP, SOME/IP and other protocols or application forms.
On-board Ethernet framework
Among them, AVB is an extension of traditional Ethernet functions, which enhances the real-time performance of traditional Ethernet audio and video transmission by adding precise clock synchronization, bandwidth reservation and other protocols, and is a network audio and video real-time transmission technology with great development potential. SOME/IP (Scalable Service-Oriented MiddlewarE on IP) specifies the video communication interface requirements for vehicle camera applications, which can be applied to the field of vehicle cameras, and realizes the mode control of driver assistance cameras through apis.
As an extension of AVB protocol, Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) introduces related technologies of time-triggered Ethernet, which can efficiently realize the transmission of automotive control information. In addition, the on-board Ethernet of the 1Gbit communication standard also supports Power Over Ethernet (POE) function and Energy-Efficient Ethernet (EEE) function. The POE function provides power for connected terminal devices while transmitting data through twisted pair cables, eliminating the need to connect external power cables to terminals and reducing the complexity of power supply.
On-board Ethernet standardization
In terms of in-vehicle Ethernet standardization, the IEEE802.3 and IEEE802.1 working groups, AUTOSAR, the OPEN Alliance and the AVnu Alliance have played a major role in promoting it.
The IEEE802.3 local area network standard represents the mainstream Ethernet standard in the industry, and the on-board Ethernet technology is developed on the basis of IEEE802.3, so the IEEE is currently the most important international standardization body for on-board Ethernet. In order to meet the requirements of the car, it involves the development of a number of new specifications and the revision of the original specifications within the two working groups of IEEE802 and 802.1, including PHY specifications, AVB specifications, and single-wire to data line power supply. In addition, AVB related to AV transmission, timing synchronization and other specifications also need to be standardized by other technical committees of IEEE, such as IEEE1722 and IEEE1588.
OPEN Alliance
The OPEN Industry Alliance was launched in November 2011 by Broadcom, NXP, and BMW to promote the application of Ethernet-based technology standards to in-car connectivity. The main standardization goal is to develop a 100Mbit/s BroadR-R physical layer standard and develop OPEN interoperability requirements.
AUTOSAR
AUTOSAR is a consortium of automotive manufacturers, suppliers, and tool developers that aims to develop an open, standardized automotive software architecture, and the AUTOSAR specification already includes the automotive TCP/UDP/IP protocol stack.
AVnu
The AVnu Alliance was formed by Broadcom in collaboration with Cisco, Harman and Intel to promote the IEEE 802.1 AVB standard and the Time Synchronization Network (TSN) standard, establish a certification system, and address important technical and performance issues such as precise timing, real-time synchronization, bandwidth reservation, and traffic shaping.
Vehicle Router,Vehicle 4G Router,Vehicle 4G Wireless Router,Vehicle Wifi Router
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szmovingcomm.com