Doing a simple mathematical calculation, it is easy to understand why government agencies and mobile phone manufacturers have to actively reduce the standby power consumption of mobile phone chargers: there are more than 4 billion mobile phone users worldwide, and most of them are used to Even after the battery is fully charged and the phone is unplugged, it still keeps its charger connected and will continue to consume power. According to Nokia's statistics, 2/3 of the power used during mobile device use is consumed in no-load mode.
For everyone, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel consumption is very important, but in addition, mobile phone charger solutions must also have practical advantages, such as reasonable cost, easy design, production and Reliable quality. In this regard, Fast Semiconductor can provide designers with various related ICs. These products use the company's expertise in integration and packaging to integrate a PWM controller and a MOSFET on a single component (if needed) And a number of protection functions can help manufacturers meet the 5-star energy-saving requirements, that is, no-load power consumption is less than 30mW (only 1/10 of the industry's average power consumption of 300mW) and ± 5% output CV / CC tolerance , And no secondary side control circuit is needed.
Strict no-load tolerance (Tolerances)
Today ’s mobile phone users have many requirements, including large touch screens, multi-megapixel cameras, Bluetooth and 802.11 wireless links, comprehensive web browsing, e-mail and database access, GPS navigation, music And video downloads, as well as future mobile digital TV. All these popular features require the use of electrical energy. The mobile phone is powered by a battery, and the battery can be charged by a variety of different power sources, such as a cigarette lighter (power converter) on a car, a power socket on an aircraft seat, and a laptop or desk USB port on the upper computer.
Of course, the most common charging power source is the AC power socket on the wall and an external AC-DC power adapter (adapter) usually called a mobile phone charger (however, most of these devices are not real chargers. Charging The circuit is actually inside the phone).
Mobile phones require only 2W of power on average, while laptops require nearly 100W, which is why cell phone chargers are much smaller than laptop chargers. Nevertheless, as there are as many as 4 billion mobile phone users worldwide, and only 1 billion people have PCs, reducing power consumption, which is the standby power consumption known to ordinary users or the no-load power consumption known to engineers, has become a Key design considerations.
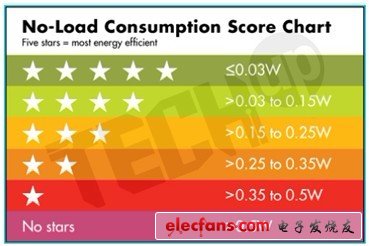
The need to take a series of measures to improve efficiency and reduce no-load power consumption is the result of these concerns. The latest and most stringent is the voluntary Star RaTIng System agreement proposed by the top five mobile phone manufacturers in the world to identify when the charger is still plugged into a wall socket after charging is completed Consume energy. The star system starts from 0 stars to the highest 5 stars. A charger with a rated standby power consumption> 0.5W under no load is a 0-star mark, and a standby power consumption <0.03W 30mW) is a 5-star rating (see table). By comparison, the standby power consumption of most existing mobile phones falls within the range of 150-300mW.
This is very important, and it is necessary to reiterate: To obtain a 5-star mark, the charger must reach no-load power consumption of 30mW or less (see table), which is higher than that of Energy Star (level V). The requirements are still 90% lower.
The importance of strict CV / CC tolerance
Currently, lithium-ion technology is used for the batteries of small portable devices. The advantages of this technology are its small size, high energy density, small self-discharge, and great flexibility in size and shape. Lithium-ion batteries are generally suitable for constant current / constant voltage (CC / CV) charging methods; the length of each charging mode depends on the battery capacity and the performance of the charger.
In the most basic form, when the battery voltage is very low, the charger enters a constant current (CC) charging mode; then most of the charging energy is transferred to the battery. Once the battery is charged to a floating voltage (the battery is disconnected, the battery voltage is usually around 4.2V at zero current), the system will begin to reduce the charging current to maintain the required voltage-this is the so-called "constant voltage" mode.
Although it is relatively simple to implement, when charging the mobile phone, it is necessary to accurately control the floating voltage region to obtain the maximum battery capacity and extend the battery life. Inaccurate battery voltage regulation may cause the battery to be undercharged, resulting in a significant reduction in battery capacity. On the Other hand, if the charging voltage is too high, the cycle life of the battery will be greatly shortened. Overcharging of lithium-ion batteries can also cause catastrophic failure of equipment.
Guangzhou Etmy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.digitaltalkie.com