
That's right, when you think of TI's state-of-the-art microcontroller MSP430, low power is one of the first things that comes to mind. After all, this is why the MSP430 is so popular in battery-powered applications. You can extend the battery life of your app by limiting battery drain. Given the slow pace of lithium-ion battery technology, it is imperative to achieve the best battery life for your application by limiting power consumption.
This is very intuitive.
If I tell you to add an extra component, can you save 30% or more of the power? That's right, adding an add-on does help to extend battery life by a few hours. I know you will definitely think this is a bit unbelievable. But I can guarantee that this is entirely possible.
This is where the regulator comes in.
Often in small portable applications, the easiest way to do this is to connect the MSP430 directly to the battery. After all, the MSP430 has a wide operating voltage (1.8 to 3.6V), depending on how much frequency you want your kernel to run. As shown below.
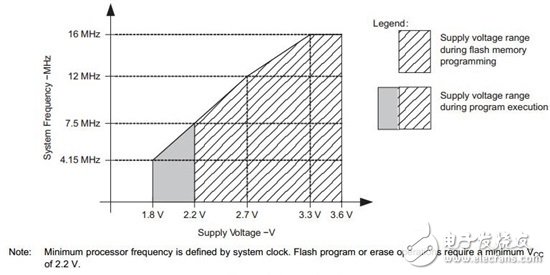
For example, we can power the MSP430F2274 with two 1.5V alkaline button batteries without any additional regulation. The 3V power supply provided by the battery powers the MCU at almost all system frequencies. However, a minimum 3.3V supply voltage is required to operate the system at 16MHz.
Things become interesting when looking at the flow losses of different supply voltages (system frequency combinations). See Figure 2 below and Figure 3 below:

At a glance, you will understand that at a certain frequency, if you increase the power supply voltage, the current consumption will increase. Conversely, if we keep the supply voltage constant and increase the operating frequency, the flow rate will also increase. The main conclusion from the above observations is that the method of powering the MSP430 has high efficiency and low efficiency. If you increase the supply voltage, you may consume more unnecessary current.
Let's go back to the example. If a 3V supply is used to power the MSP430 running at 1MHz, we expect the operating mode current to be 390uA as shown in the following table. But keep in mind that at 1MHz, if we don't plan the programming flash, the operating voltage can be any value between 1.8 and 3.6V. If the supply voltage is reduced from 3V to 2.2V, the current consumption will drop to 270uA. This is more than 30% reduction in flow consumption! Think about how this affects battery life.

Flow rate at different operating frequencies
The regulator helps to achieve this efficiency. The regulator reduces the current drawn by the MCU by reducing the supply voltage provided by the battery.
Next week we will discuss which regulators can be used to take advantage of this performance. By reducing the voltage supplied to the MSP430, we minimize the flow. But not any regulator can do this. Optimizing the application battery life requires everyone to work hard.
AMOLED Smart Watch
AMOLED Smart Watch
everyone enjoys luck , https://www.eeluckwatch.com