When service robots are used in homes, hotel rooms, office spaces, clubs, and other indoor spaces, obstacle avoidance sensors must be used, usually using one or more of the four sensors: infrared, ultrasonic, laser radar, and binocular vision. Obstacle avoidance operation, this article will mainly analyze the installation position of the infrared obstacle avoidance sensor.
Infrared obstacle avoidance sensor basic principle: the use of the object's reflective nature. In a certain range, if there are no obstacles, the infrared rays emitted will gradually weaken as the distance traveled, and eventually disappear. If there is an obstacle, the infrared light encounters an obstacle and is reflected to reach the sensor receiving head. When the sensor detects this signal, it can confirm that there is an obstacle in front of it, and sends it to the SCM. The SCM performs a series of processing and analysis, coordinates the two rounds of work of the service robot, and completes the obstacle avoidance action.

The infrared obstacle avoidance sensor is a distance-adjustable obstacle avoidance sensor designed for a wheeled robot. It has a pair of infrared transmitting and receiving tubes, and the transmitting tube emits a certain frequency of infrared rays. When the detection direction encounters an obstacle (reflecting surface), the infrared rays are reflected back by the receiving tube. At this time, the indicator lights up and is processed by the circuit. The signal output interface outputs digital signals. The potentiometer knob can be used to adjust the detection distance. The effective distance is 2-40cm and the working voltage is 3.3V-5V. Due to the wide range of operating voltage, it can still be stable under the condition of relatively large power supply voltage fluctuations. Work, suitable for a variety of single-chip, Arduino controller, raspberry pie, installed on the robot can sense changes in the surrounding environment.

A typical infrared barrier sensor
Infrared obstacle avoidance sensor working principle: red line is connected to 5V, yellow is connected to the signal, green GND is connected to the negative pole of the power supply or the logic ground on the MCU. Front accessible output high level, obstacle output (yellow) level will change from high to low (0). The rear view has a potentiometer to adjust the detection distance of the obstacle. In the circuit design, the output yellow line can be added with a pull-up resistor of 10K to 5V, and then it can be connected to the SCM to detect it. It will be relatively stable. The SCM detection can be implemented using an external hardware interrupt such as INT0 INT1.
The infrared obstacle avoidance sensors currently installed on the service robot body are installed in accordance with the high, medium and low three groups. For example, the most common installation height is a low 80mm, a medium 480mm, and a high 780mm. There is no sufficient standard and basis for the installation height setting. There are many cases in practical applications. The infrared obstacle avoidance sensor cannot detect nearby obstacles because the installation is too high, too low or the density is not enough, thus affecting the service robots. Actions and damage to the environment and people may be caused by inappropriate installation methods of infrared obstacle avoidance sensors. It is urgent to study more suitable deployment plans for infrared obstacle avoidance sensors based on the characteristics of the environment, especially the characteristics of obstacles.
Guangzhou Zero Software Technology Co., Ltd. (Robot Zero) conducted a large number of real-world measurements and scene simulation during the R&D of health care service robots, basically summarizing the installation height of infrared sensors required for serving robots in residential and other indoor spaces. These experiences are also used on the body of the Siberian Husky Health Service robot.
In research and development, we have organized and summarized common furniture heights based on national standards and specifications related to furniture design, especially analysis of furniture projections such as tables, chairs and backs, coffee tables, sofa armrests and backrests, and bedsides. Because these are beyond the bottom and the protruding part in the vertical plane, it is the easiest to bring obstacles to the movement of the service robot.

The following is a dimensional description of the height of the furniture:
1, table-type furniture height standards can have 700mm, 720mm, 740mm, 760mm four specifications;
2? The seating height of the chair and stool can have three specifications of 400mm, 420mm and 440mm.
3? The general height of the bed is 45 centimeters; the face is measured from the height of the ground, the standard is 46 to 50 centimeters;
4? General seating height of the sofa: 350-420mm; armrest height 560-600mm; single-person back height: 700-900mm.
5, coffee table height is about 350-500mm.
The other furniture in the room, including cabinets, boxes, bookshelves, etc., are all basically the same in the vertical plane without obvious protruding parts, so the service robot infrared sensor is consistent in the distance measured at any height, as long as any height The acquisition of data by infrared sensors can represent the perception of this obstacle. Therefore, such furniture with flat facades does not need to consider the new installation method of infrared obstacle avoidance sensors.
Home appliances, especially some home appliances that may appear on the attachment path of service robots, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and drinking fountains, also have flat facades, so there is no need to consider new installation methods for infrared obstacle avoidance sensors.
Because the thickness of the desktop plate of the furniture has three main dimensions of 16mm, 18mm, 25mm, etc., the thickness of the tempered glass of the coffee table is 10mm or more, usually 12mm. Therefore, I can touch the convex surface of the furniture from the furniture surface (the highest point of the furniture height) downwards by 10mm. This can be an important basis for the installation height of the infrared obstacle avoidance sensor for the service robot.
According to the characteristics of the furniture, we have sorted out some heights that are sensitive to the actions of the service robot:
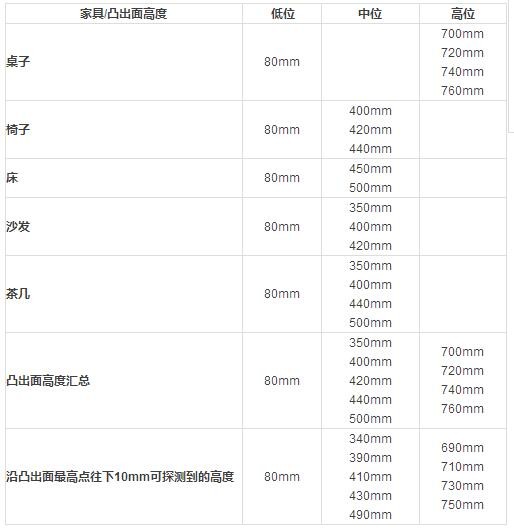
Therefore, from the above table, it is possible to obtain the low, medium, and high positions of the service robot installed with the infrared obstacle avoidance service robot. With the height of the installation, it is also necessary to further design the layout of the infrared avoidance obstacle sensor.
In order to obtain the best obstacle avoidance effect, we used a total of 24 infrared obstacle avoidance sensors, including 12 on the front side, 3 on each side of the two sides, a total of 6 and 6 on the back.
The low-level infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are distributed at a height of 80 mm, with two frontal deployments, one on each side of the two sides and two on the back.
The median infrared obstacle avoidance sensor is distributed at five different heights, which are 340mm, 390mm, 420mm, 430mm, and 490mm. Among them, five infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are required to be deployed and installed at five heights. One infrared obstacle avoidance sensor is installed on the side, and the height is 420 mm. Three infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are installed on the back with heights of 340 mm, 390 mm, and 420 mm, respectively.

The high-level infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are installed at four different heights, namely 690mm, 720mm, 730mm, and 750mm. Among them, four infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are required to be deployed and installed at all four heights. One infrared obstacle avoidance sensor is installed on the side and the height is 720 mm. Two infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are installed on the back with heights of 690 mm and 730 mm, respectively.
In this case, the infrared obstacle avoidance sensor uses an NPN type photoelectric switch; the output state is 0, 1, ie, the high level and the low level in the digital circuit, the detected target is a low level output, and the normal state is a high level output. , Output plus a 1K pull-up resistor can be connected to the microcontroller IO port. Since 24 infrared obstacle avoidance sensors are designed, the number of IOs required for the corresponding microcontroller is 24.
This installation position and installation method is an important improvement over the existing installation method of the infrared evacuation sensor: the installation position of the height of the furniture projection is optimized, and a total of 24 infrared sets of low, medium, and high installation areas are used. Obstacle avoidance sensors are distributed on the front, sides, and rear of the service robot. The infrared obstacle avoidance sensor can always scan the convex surface of the furniture, so that the service robot can effectively avoid all kinds of furniture, and is suitable for various service robots such as home service robots, commercial service robots, food delivery robots, and the like.
2000Puffs Disposable Vape,2000Puffs Disposable Pod Pen Device,Airis Mega E-Cigarette,Airis Mega Pod Pen Device
Shenzhen Uscool Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.uscoolvape.com