This article is mainly about the introduction of LED lights, and focuses on the detailed description of the timer-based LED light circuit diagram.
LED lightsThe LED lamp is an electroluminescent semiconductor material chip, which is cured on the bracket with silver glue or white glue, and then connects the chip and the circuit board with a silver wire or gold wire. The surrounding is sealed with epoxy resin to protect the inner core wire. Function, finally install the shell, so the LED lamp has good seismic performance.
Features
1. Energy saving: the energy consumption of white LED is only 1/10 of that of incandescent lamps and 1/4 of that of energy-saving lamps.
2. Longevity: The life span can reach more than 100,000 hours, which can be described as "one-time-for-all" for ordinary household lighting.
3. It can work at high speed: if the energy-saving lamp is frequently turned on or off, the filament will turn black and quickly break down, so it is safer.
4. Solid-state packaging belongs to the type of cold light source. So it is easy to transport and install, and can be installed in any miniature and enclosed equipment without fear of vibration.
5. LED technology is advancing with each passing day, its luminous efficiency is making amazing breakthroughs, and the price is constantly decreasing. The era of white LEDs entering the home is rapidly approaching.
6. Environmental protection, no harmful substances of mercury. The assembly parts of the LED bulb can be easily disassembled, and can be recycled by others without recycling by the manufacturer.
7. Light distribution technology expands the LED point light source into a surface light source, enlarges the light-emitting surface, eliminates glare, sublimates visual effects, and eliminates visual fatigue.
8. Integrated design of lens and lampshade. The lens has the functions of concentrating and protecting at the same time, avoiding the repeated waste of light and making the product more concise and beautiful.
9. High-power LED flat cluster packaging, and integrated design of radiator and lamp holder. It fully guarantees the heat dissipation requirements and service life of the LED, and fundamentally meets the arbitrary design of the structure and shape of the LED lamp, which has the distinctive characteristics of the LED lamp.
10. Significant energy saving. Using ultra-bright and high-power LED light source, with high-efficiency power supply, it can save more than 80% of electricity than traditional incandescent lamps, and the brightness is 10 times that of incandescent lamps under the same power.
11. Ultra-long life of more than 50,000 hours, which is more than 50 times that of traditional tungsten filament lamps. The LED adopts a highly reliable advanced packaging process-eutectic welding, which fully guarantees the long life of the LED.
12. No flicker. Pure DC work eliminates visual fatigue caused by traditional light source strobe.
13. Green and environmental protection. It does not contain lead, mercury and other polluting elements and does not pollute the environment.
14. Impact resistance, strong lightning resistance, no ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. There is no filament and glass shell, there is no broken problem of traditional lamp tube, no harm to human body, no radiation.
15. Work under low thermal voltage, safe and reliable. Surface temperature≤60℃ (when ambient temperature Ta=25℃).
16. Wide voltage range, universal LED light. 85V~264VAC full voltage range and constant current, to ensure that the life and brightness are not affected by voltage fluctuations.
17. Using PWM constant current technology, high efficiency, low heat, and high precision of constant current.
18. Reduce line loss and no pollution to the power grid. The power factor is ≥0.9, the harmonic distortion is ≤20%, and the EMI conforms to the global index, which reduces the power loss of the power supply line and avoids high-frequency interference and pollution to the power grid.
19. The universal standard lamp holder can directly replace the existing halogen lamp, incandescent lamp and fluorescent lamp.
20. The luminous visual efficiency rate can be as high as 80lm/w, a variety of LED lamp color temperatures are available, high color rendering index, and good color rendering.
Obviously, as long as the cost of LED lights decreases with the continuous improvement of LED technology. Energy-saving lamps and incandescent lamps will inevitably be replaced by LED lamps.
The country pays more and more attention to lighting energy saving and environmental protection issues, and has been vigorously promoting the use of LED lamps.
Pros and cons
* Heat dissipation problem, if the heat dissipation is not good, the life span will be greatly shortened.
* The power saving of low-end LED lamps is still lower than that of energy-saving lamps (cold cathode tubes, CCFL).
* The initial purchase cost is higher.
* Due to the strong directivity of the LED light source, the special optical characteristics of the LED need to be considered in the design of the lamp.
The following is for the comparison between neon lights and LED lights, adding the latest LED technology to compare, not the information that everyone has seen on the Internet before.
1. Does the LED light source have a life span of 100,000 hours?
According to the light decay of 7%, it is actually only about 50,000 hours. According to the light attenuation of 3%, the actual use can reach 80,000 hours.
2. Does the LED heat up?
Yes, heat dissipation is required.
3. Can LED replace incandescent lamp?
The luminous flux, luminous efficiency and color rendering are OK, but too expensive and will not decline in recent years. However, the cost of replacing incandescent lamps can be reduced by increasing the luminous flux of the product.
4. Can LED be used simply as an ordinary light source?
No, you need to drive the power supply, the optical LED light and the heat conduction.
5. Comparison of the performance and advantages of the two light sources
The advantages of neon lights have been covered by LEDs, but LED lights are too expensive.
6. Comparison of the power supply of the two light sources
The low voltage of LED is good, but the current is too large. The input current of a large 1W LED single lamp is 350mA.
7. Comparison of the control technology of the two light sources
LED is easy to implement, but neon lights are mature.
8. Comparison of the stability of the two light sources
The LED is not consistent, and the neon light is quite stable. A small number of manufacturers can achieve relative stability, such as combining CREE and AOD chips to take advantage of their respective chips.
9. Price comparison of the two light sources
LEDs are more expensive, but yellow and red are quite the same, and the main one is white LED.
10. Comparison of two kinds of light sources for outdoor use
LED lights have been completely waterproof and dustproof.
11. Comparison of the two light source markets
The annual output value of global lighting products is 42 billion U.S. dollars (China 15 billion U.S. dollars) LED light sources now account for less than 1%.
The production of the circuit diagram of the LED lamp based on the timerUse timer 0 to work in mode 1 (16-bit counter) to realize the flashing of LED lights. Let's take a look at the logic structure diagram of timer 0 working in mode 1.
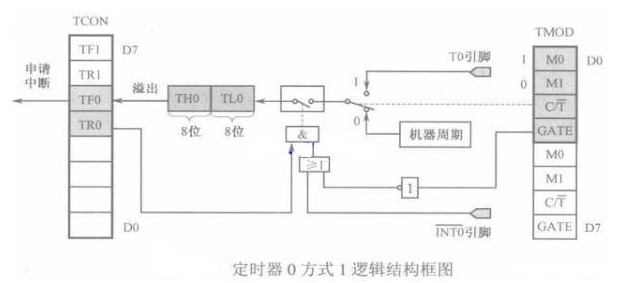
As can be seen from the above figure, GATE passes through the NOT gate first, and then uses the INT0 pin as the input of the OR gate. Here is a brief mention of AND gates, OR gates and NOT gates in digital circuits. As the name implies, the output of the AND gate is high if and only when all inputs are high. As long as one of the inputs is high, the output of the OR gate is high. The output level state of the NOT gate is just the same. The input level state is opposite. Therefore, from the logic structure diagram of timer 0 mode 1, when GATE=0 and TR0=1, the low 8-bit register of TL0 starts to count up under the action of the machine cycle. When TL0 is full, carry to TH0 until TH0 is also full. At this time, there is another count, the counter overflows and TF0 is set to 1, and a timer 0 interrupt request is issued.
After knowing how the timer works, the key point is how to make the timer time the time we want? This involves the initial value of the timer. Once the timer is started, it starts to add 1 every other machine cycle on the basis of TL0 and TH0 until it overflows. Assuming that the initial values ​​of TL0 and TH0 are 0 at the beginning of the program execution, and the crystal oscillator of the single-chip microcomputer is 12MHz, then the machine cycle of the single-chip microcomputer is 1us, and a total of TL0 and TH0 are required (2 to the 16th power minus 1=65535) Count, add 1 to another one to overflow. That is to say, the maximum time that the timer can time is 65536us (65.536ms). It is conceivable that if we need the timer to be able to time 50ms, then TL0 and TH0 must have certain initial values. Popular understanding is that the 16-bit counter of the timer is a bucket. This bucket can fill up to 65.536 kilograms of water, and we only need to fill the bucket with 50 kilograms of water to fill the bucket. At this time, there must be 15.536 kilograms of water in the bucket. , This is the initial value.
Okay, here we formally start how to determine the initial value of the timer. We want the timer to generate an interrupt at 50ms. At this time, the total number of TL0 and TH0 is 65536-50000=15536, and 15536 ​​is modulo 256: Load 15536/256=60 into TH0, and add 15536 ​​to 256 remainder: 15536%256=176 into TL0. This will get the initial value we want.
So why is it counted like this? It has been said before that Timer 0 is a 16-bit counter when working in mode 1. TH0 is the upper 8 bits and TL0 is the lower 8 bits. The initial values ​​of TL0 and TH0 are shown in the figure below when the microcontroller is reset. The value of each bit is It is binary (either 0 or 1). When TL0 is full, carry to TH0. After TH0 is full, add 1 to apply for timer interrupt.
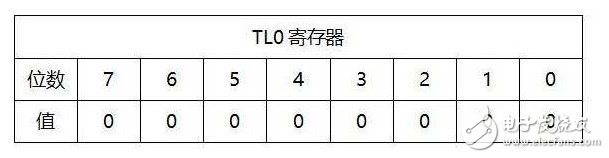
When TL0 counts up once, the 8-bit value is 1, which is 255 (2 to the 8th power minus 1). When TL0 is increased by 1, all TL0 is cleared and carried to TH0, which means that the value in TL0 is 0000 0000. , And the value in TH0 is 0000 0001, this time it is counted 256 times; the same wait until the second count of TL0 is full, the 8-bit value is 1, and then add 1 when TL0 is all cleared and carried forward to TH0, that is to say At this time, the value in TL0 is 0000 0000, and the value in TH0 is 0000 0010, this time is counting 2*256 times, and so on, overflow when 256*256 times are counted. Do you see the pattern?
Ok, let’s continue to talk about any situation. Assuming that the initial value in TL0 is decimal L and the initial value in TH0 is decimal H, then after (256-L) counts, the value in TH0 plus 1 becomes H+1 , The value in TL0 becomes 0; after 256 counts, the value in TH0 becomes H+2, and the value in TL0 becomes 0. By analogy, when TH0 is added (256-H) times 1, an overflow occurs, and the timer requests an interrupt.
Therefore, a total of [(256-H-1)*256+256-L]=(65536-256H-L) count timer request interrupts have passed. That is to say, the initial value of the 16-bit register in the timer C=256H+L.
Obviously, the initial value H=C/256 in TH0, and the initial value L=C%256 in TL0, this is derived.
After getting the timer's initial value, we can write the timer interrupt code.
How to write interrupt service routine
The interrupt function format of C51 is as follows:
void function name () interrupt interrupt number using working group
{
The specific content of the interrupt service program
}
The interrupt function has no return value and parameters. As long as the function name conforms to the C language standard, the interrupt number refers to the interrupt source serial number in the microcontroller, which is the only credential for the compiler to identify different interrupt sources. The using working group refers to the use of this interrupt service program Which of the 4 groups of working registers in the MCU memory is automatically allocated by the compiler, usually we can ignore it.
After talking so much, I can finally write a program, isn't it a little excited?
#include //Include header files
sbit led = P0^0;
unsigned char count = 0; //Time accumulation variable, we need 1000ms timing, 50 * 20 = 1000
//count is a global variable. In layman's terms, the value keeps the most recent value each time the program is re-executed
//The follow-up will specifically talk about some basic knowledge of the C language
void main()
{
TMOD = 0x01; //Set timer 0 working mode 1, 16-bit count
TH0 = (65536-45872) / 256; //Crystal oscillator 11.0592MHz, the initial value of TH0 when the timing is 50ms
TL0 = (65536-45872)% 256; //Crystal oscillator 11.0592MHz, the initial value of TL0 when the timing is 50ms
EA = 1; //Turn on the total interrupt
ET0 = 1; //Enable timer 0 interrupt
TR0 = 1; //Start timer 0
while(1); //The program stops and waits for the timer 0 interrupt to occur
}
void T0_INT() interrupt 1 //Look at the above format
{
TH0 = (65536-45872) / 256; //Crystal oscillator 11.0592MHz, the initial value of TH0 when the timing is 50ms
TL0 = (65536-45872)% 256; //Crystal oscillator 11.0592MHz, the initial value of TL0 when the timing is 50ms
//Reinstall the initial value, this is easy to understand, we need the same timing every time
count++; //Every time an interrupt is entered, that is to say, the time of 50ms is up, the count variable is accumulated
if(20 == count) //1000ms timing time is up
{
count = 0; //Clear to make it possible to time again for 1000ms
led = ~led; //P0.0 level is reversed, and the LED light is turned off or on
}
}
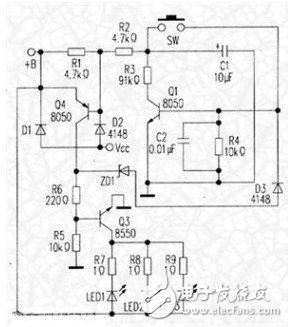
The LED desk lamp circuit is shown in the figure below, and the working principle is as follows:
â—Lighting process: When the light is off normally: C1 is charged from +B (+B is the lead battery voltage) to +B through R1, R2, and R3. At this time, the light is off and it is in the standby state. When in use, when SW is pressed and then released, the positive pole of C1 is shorted to the b pole of Q1, and the negative pole of C1 is connected to the e pole of Q1. Since the voltage across C1 is +B and cannot change suddenly, the voltage of Q1 is very high due to Ube1. After Q1 is saturated, its C pole potential is almost 0V, and +B is added to the b pole of Q4 through the partial pressure of R1 and R2, and Ube4 is forward biased, so Q4 is quickly saturated and turned on, making Q4’s The C pole potential is almost +B. It has two effects: one is to make the voltage stabilizer ZD1 (voltage value is about 2.5V) reverse breakdown, D3 forward conduction, and then the remaining voltage is added to the b pole of Q1, so that Q1 maintains saturation and realizes self-protection . The second is that this +B voltage is added to the b pole of Q3 through the partial pressure of R6 and R5, so that Q3 is also saturated and turned on, so the high-brightness LED has current flowing and emits light, and the light starts to illuminate. Q1 maintains saturated conduction due to self-protection. Its C pole potential is almost 0V, then C1 discharges through R3 and Uce1 to make its both ends voltage 0V.
â—Closing process: If you press SW again and release it in the lighting state, since the voltage across C1 is 0V, the be junction voltage of Q1 is 0V and cut off, and the c pole of Q1 becomes +B potential due to the cutoff of Q1. The b pole of Q4 is also +B potential due to the partial pressure of R1 and R2, and the be junction of Q4 is turned off due to a 0V bias. The c pole of Q4 loses the +B voltage to cut off Q3, and the three LEDs go out without current (the light is turned off). At this time, C1 is charged by +B through R1, R2, and R3 to prepare for the next action.
â—In the charging state: the charger's DC power supply Vcc is connected to +B through D1 to charge the lead storage battery. At the same time, Vcc is added to the b pole of Q4 through D2, so that Q4 remains in the cut-off state. At this time, even if SW is pressed, whether Q1 is On or off, Q4 is off, so Q3 is also off, and the three LEDs do not light up without current. So as not to affect charging.
â—When the lead battery is fully charged, the measured +B voltage is 4.2V. In order to make Q1 maintain saturation conduction (self-protection) when in use. +B must be greater than Uce4+Uzd1+UD3+Ube1=0.2+2.5+0.6+0.6=3.9V; when the +B voltage drops below 3.9V during use. It is not enough to reverse breakdown of ZD1 and make Q1 unable to realize self-protection. The phenomenon at this time is that after pressing the SW, the 3 LEDs will flash or stay for a few minutes and then go out. Many people mistakenly think that the lights are broken. In fact, it should be charged at this time. It is not malfunctioning.
Since +B is only 4V. Therefore, the circuit works under low voltage conditions. General components are not easy to damage, only Q3 and R7, R8, and R9 work with large currents, so they should be considered when repairing.
The low-cost and high-performance LED lighting circuit diagram puts forward the new concept of "steady current" in the utility model patent "a low-cost and high-performance LED lighting circuit". If this concept is recognized by experts, the concept is from electronics Angle can be said to "fill in a conceptual gap", even though it hasn't been very useful before. In the utility model patent "a low-cost and high-performance LED lighting circuit" the new concept of "steady current" is proposed. If this concept is recognized by experts, this concept can be said to "fill in one item" from the perspective of electronics. Conceptual blank", even though it didn’t have much use before.
1. "Filtering" and "Stabilization"
After the advent of AC power, there is a need for AC to DC. To get a DC power supply from AC, we have to rectify it first, but the voltage obtained by the rectified output is a half-sine wave, so there is a simple way to connect a capacitor in parallel at the output end to store the charge. This is filtering. For loads that do not require high power fluctuations, only filtering is enough, but for circuits that require voltage to reach the voltage of the battery, the filtering is not enough, and it must be stabilized.
The best active filter circuit in the filter circuit can get a power supply similar to DC, but it is still not a regulated power supply. Because its output voltage is close to DC, but it will increase with the increase of input AC voltage and decrease with the increase of load current. But the output voltage of the regulated power supply will not have this change.
Simple stabilized power supply, in order to ensure the stability of the output voltage, when the input voltage rises, it must consume excess power on the stabilized circuit. Therefore, the stabilized power supply will generate heat, while the filter power supply will generate less heat. Much.
2. "Constant current" and "constant current" In some electronic circuits, due to certain needs, we need to provide a constant current instead of a stable voltage, so a "constant current power supply" is produced.
But there is another type of component, which does not allow large current fluctuations, that is, it cannot over-current, but it can also work with a small current. For example, LED is such a component. At this time, we only need to provide it with a current that basically does not fluctuate. This unfiltered current source is called a "steady current source", and this type of current or making a current of this type is called a "steady current".
3. Comparison of the four concepts "Stable current" and "filtering" are very similar, but the difference is that the object of steady current is current, while the object of filtering is voltage; "Constant current" is very similar to "Stabilization". But it is also the same difference. The object of constant current is current, while the object of voltage stabilization is voltage.
"Stable current" increases the output current as the input current increases; "filtering" increases the output voltage as the input voltage increases.
The "constant current" input current increases to increase the input voltage, but the output current does not change; the "regulated" input voltage changes, and the output voltage does not change. Note: This kind of "steady current circuit" mentioned here is proposed in the patent "a low-cost high-performance LED lighting circuit, whether it is the first to be verified. Other "steady current circuits" generally refer to adjustable "constant current Circuit".
ConclusionThis is the end of the related introduction about LED lights. I hope this article will give you a deeper understanding of LED lights.
Related reading recommendation: Homemade 12vled lamp circuit diagram Related reading recommendation: Making LED electronic birthday candle circuit diagram and working principle analysisWhat`s the main features appear into your mind when you look yoga laptop? Lightweight, super thinner, touch screen, 360 rotating, smaller size, like as notebook? You are right, that`s the main reasons why some people also called it as laptop yoga slim or yoga notebook. To OS, just same as Education Laptop-windows operating system, so you can see many windows yoga laptop at the market around the world. In fact, this intel yoga laptop usually is designed for normal jobs, like basic WPS, Photoshop, video or music editing, online learning, shopping, presentation when on a business trip, etc. At our store, you can see 11.6 inch n5100 360 Laptop in metal, 13.3 inch 360 flip laptop, and 14 inch 360 degree rotating laptop, etc. The people who take business trips often or prefer fashion design should like this type device.
There are education laptop also, like 14.1 inch Student Laptop for Hope or government Projects, 15.6 inch competitive celeron business laptop for normal business works, 15 inch 10th or 11th Gaming Laptop for heavier tasks, like teachers, high or university students, etc, 16.1 inch i7 16gb ram 4gb graphics laptop for engineering student, etc
Any other question or other requirements, just contact us freely.
Yoga Laptop,Laptop Yoga Slim,Yoga Notebook,Intel Yoga Laptop,Windows Yoga Laptop
Henan Shuyi Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.shuyilaptop.com