Nowadays, the camera of smart phones has changed dramatically in terms of hardware and camera performance. In the past, the camera of our mobile phone was still in the stage of 300,000 and 2 million pixels, but in the blink of an eye, the mobile phone camera has reached the mainstream of 8 million. It's even 13 million. In addition to the improvement in pixels, another core component of the camera, the sensor of the camera has also made great progress. The cameras of mainstream mobile phones now use two types of sensors, back-illuminated and stacked. What's the difference? Next, the author will give you some popular science.

Back-illuminated sensor
First, let's take a look at the difference between the popular back-illuminated sensors and the traditional ones. The entire photodiode of the sensor of the traditional camera is located at the lowermost layer of the photosensitive chip, and the A / D converter and amplifier circuit of the sensor are located at the upper layer of the photodiode. Even higher.
In addition, the circuit connection layer on the upper layer of the traditional photosensitive chip will also reflect light, affecting the intensity of light reaching the photodiode, thereby reducing the amount of light received by the sensor. Therefore, under normal circumstances, the traditional camera sensor takes no problem when the daylight is sufficient, but the performance will be a bit "stretched" in the case of low light, and it is difficult to shoot brightly in low light. , Good quality photos.
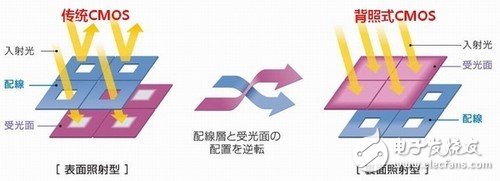
Comparison of traditional and back-illuminated CMOS structures
In order to improve this situation, the back-illuminated sensor has its significance. Compared with the ordinary sensor, the camera equipped with the back-illuminated sensor can increase by about 30% -50% in low light environment. Sensitivity, capable of taking higher quality photos in low light.
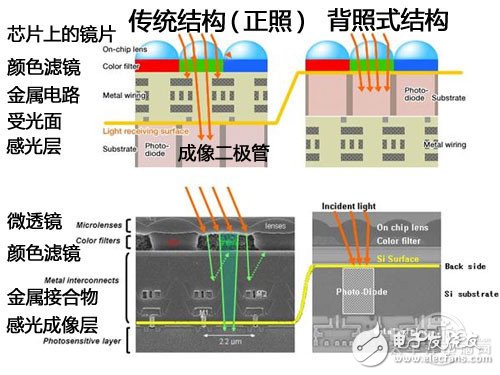
Back-illuminated sensor structure diagram
So why can the sensitivity of the back-illuminated sensor increase so much? That's because the back-illuminated sensor is simply thinner than previous sensors, with better image quality and lower noise. It interchanges the position of the photosensitive layer and the substrate, and directly contacts the light-transmitting surface, thereby reducing the loss of light in the middle link, and each corresponding pixel surface on the light-transmitting surface is changed to the form of a lens to converge more concentratedly. The external light is sent to the corresponding pixel, which reduces the unnecessary light interference between the pixels (also referred to as increasing the aperture ratio).
Jinhu Weibao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.weibaoxd.com