Abstract: This application note discusses Maxim ’s third-generation Class D audio power amplifier technology, which enables “filterless†work in consumer electronics. Specifically, this article explains Maxim's new generation of patent-pending active radiation suppression circuits that can minimize radiation without degrading audio performance.
Overview Maxim's second-generation Class D audio power amplifiers feature unique, patented spread-spectrum modulation that broadens spectral components over a wider frequency band, thereby improving radiated EMI from speakers and cables. Maxim ’s third-generation Class D audio power amplifier uses the same spread-spectrum modulation technology, and a new, patent-pending active radiation suppression circuit (AEL) is added to this technology. In the case of audio performance, the narrowband spectral components are further reduced. The combination of these two proprietary technologies allows Maxim ’s Class D audio power amplifiers (such as the MAX9705) to drive up to 24 inches of unshielded cables under "filterless" operating conditions and meet EN55022 electromagnetic interference (EMI) Normative requirements. Maxim uses AEL circuits for Class D amplifiers, while maintaining the high efficiency of Class D amplifiers while minimizing electromagnetic emissions. This article explains Maxim's technology.
Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier technology Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier features Maxim's spread-spectrum modulation technology, and a new, patent-pending active radiation suppression is added to this technology Circuit (AEL), this circuit can further reduce the narrow-band spectral components. ¹ Under all possible transient output conditions, the AEL circuit can actively control the gate transient switching process of the output FET, which greatly reduces EMI radiation. In the case of minimal impact on the efficiency of the amplifier, the active radiation suppression circuit controls the slew rate of each gate drive signal to minimize the radiation caused by the signal full swing and high switching frequency, and its negative impact may cause the amplifier The efficiency is slightly lower.
Since the high efficiency of Class D amplifiers comes from the full-swing drive of the output FET and the fast on / off transient process (Figure 1), the control of the edge rate will affect the efficiency of the Class D amplifier to some extent.
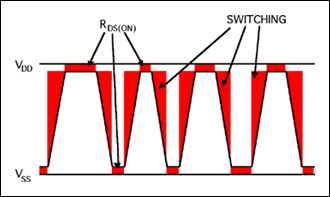
Figure 1. Class D amplifier output waveform showing the loss due to the edge rate of the switching signal and the transistor RDS (ON)
Shortening the rise and fall time of the signal can speed up the transient process and improve the efficiency of the amplifier. If the switching time is increased, the efficiency of the amplifier will decrease. When the AEL circuit is working, the gate drive signal of the output FET is intelligently managed so that the Class D amplifier can achieve the highest efficiency while improving electromagnetic radiation suppression (Figure 2).
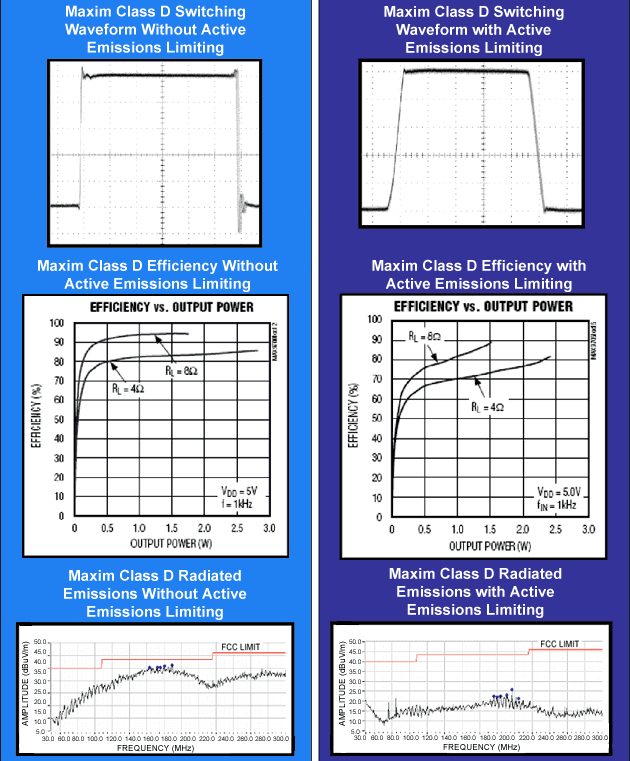
Figure 2. The active radiation suppression circuit intelligently controls the slew rate of the switching signal of the class D amplifier, effectively reducing the electromagnetic radiation of the circuit under the premise of a small decrease in efficiency.
MAX9705 Class D AEL Amplifier The MAX9705 is a mono Class D amplifier with ultra-low EMI. It uses Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier technology. When using a 12-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable, the MAX9705 can provide up to 90% efficiency, fully meet the FCC's emission limits, and leave a 15.8dB margin (Figure 3). It is particularly worth mentioning that when using 24-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cables, the MAX9705 also meets the FCC requirements (Figure 4).
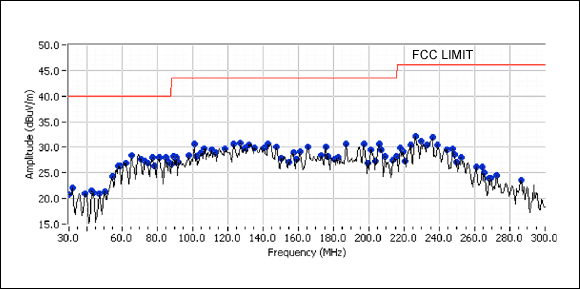
Figure 3. MAX9705 electromagnetic radiation data (tested with the MAX9705 evaluation board, spread spectrum modulation mode, using 12-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable)
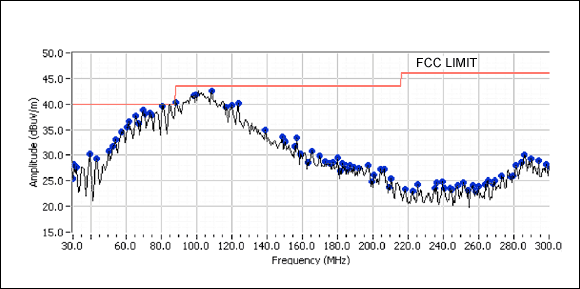
Figure 4. MAX9705 electromagnetic radiation data (tested with the MAX9705 evaluation board, spread spectrum modulation mode, using 24-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable)
In addition to excellent EMI performance, the MAX9705 IC also has a low THD + N of 0.02%, a high PSRR of 75dB, and a low-power shutdown mode of 0.3µA. The MAX9705 is available in a 10-lead TDFN (3mm x 3mm x 0.8mm) package, a 10-lead µMAX® and a 12-ball UCSP ™ (1.5mm x 2mm x 0.6mm) package. For more information, please refer to the MAX9705 data sheet .
Conclusion The electromagnetic radiation index of Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier can make Class D amplifiers truly "filter-free" in consumer electronics equipment. At the same time, spread spectrum modulation and active radiation suppression circuits (AEL) reduce the number of external components, which can effectively extend battery life. Maxim's third-generation class D amplifier can achieve the performance of class AB amplifiers without sacrificing efficiency. In addition, "filterless" technology provides a smaller, more cost-effective solution, making it ideal for cellular phones, MP3s, PDAs, and notebook computers.
Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier technology Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier features Maxim's spread-spectrum modulation technology, and a new, patent-pending active radiation suppression is added to this technology Circuit (AEL), this circuit can further reduce the narrow-band spectral components. ¹ Under all possible transient output conditions, the AEL circuit can actively control the gate transient switching process of the output FET, which greatly reduces EMI radiation. In the case of minimal impact on the efficiency of the amplifier, the active radiation suppression circuit controls the slew rate of each gate drive signal to minimize the radiation caused by the signal full swing and high switching frequency, and its negative impact may cause the amplifier The efficiency is slightly lower.
Since the high efficiency of Class D amplifiers comes from the full-swing drive of the output FET and the fast on / off transient process (Figure 1), the control of the edge rate will affect the efficiency of the Class D amplifier to some extent.

Figure 1. Class D amplifier output waveform showing the loss due to the edge rate of the switching signal and the transistor RDS (ON)
Shortening the rise and fall time of the signal can speed up the transient process and improve the efficiency of the amplifier. If the switching time is increased, the efficiency of the amplifier will decrease. When the AEL circuit is working, the gate drive signal of the output FET is intelligently managed so that the Class D amplifier can achieve the highest efficiency while improving electromagnetic radiation suppression (Figure 2).

Figure 2. The active radiation suppression circuit intelligently controls the slew rate of the switching signal of the class D amplifier, effectively reducing the electromagnetic radiation of the circuit under the premise of a small decrease in efficiency.
MAX9705 Class D AEL Amplifier The MAX9705 is a mono Class D amplifier with ultra-low EMI. It uses Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier technology. When using a 12-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable, the MAX9705 can provide up to 90% efficiency, fully meet the FCC's emission limits, and leave a 15.8dB margin (Figure 3). It is particularly worth mentioning that when using 24-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cables, the MAX9705 also meets the FCC requirements (Figure 4).

Figure 3. MAX9705 electromagnetic radiation data (tested with the MAX9705 evaluation board, spread spectrum modulation mode, using 12-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable)

Figure 4. MAX9705 electromagnetic radiation data (tested with the MAX9705 evaluation board, spread spectrum modulation mode, using 24-inch unshielded twisted pair speaker cable)
In addition to excellent EMI performance, the MAX9705 IC also has a low THD + N of 0.02%, a high PSRR of 75dB, and a low-power shutdown mode of 0.3µA. The MAX9705 is available in a 10-lead TDFN (3mm x 3mm x 0.8mm) package, a 10-lead µMAX® and a 12-ball UCSP ™ (1.5mm x 2mm x 0.6mm) package. For more information, please refer to the MAX9705 data sheet .
Conclusion The electromagnetic radiation index of Maxim's third-generation Class D amplifier can make Class D amplifiers truly "filter-free" in consumer electronics equipment. At the same time, spread spectrum modulation and active radiation suppression circuits (AEL) reduce the number of external components, which can effectively extend battery life. Maxim's third-generation class D amplifier can achieve the performance of class AB amplifiers without sacrificing efficiency. In addition, "filterless" technology provides a smaller, more cost-effective solution, making it ideal for cellular phones, MP3s, PDAs, and notebook computers.
Automatic Gas Cooker,Natural Fire Stove,Mini Cooker,Wifi Control Cooker Stove
JOYOUNG COMPANY LIMITED , https://www.globaljoyoung.com