2016 is a year of rapid development in the robotics industry. From the robot dance at the CCTV Spring Festival Gala to the major robot operating systems and control systems companies that have blossomed everywhere, from robot conferences and robot forums across the country to robotics and Internet operations. The combination of emerging technologies such as big data, robots are no longer artificial substitutes for repetitive heavy physical labor in our traditional sense, but more intelligent and common. More and more robots are entering the ordinary business, and for these companies, the performance of the robot control system is their focus.
For the time being, there is no performance test standard for industrial robot control systems. In the robot industry, performance specifications are mentioned, generally for the whole machine. There are many indicators for evaluating the performance of industrial robots. Based on different design purposes and uses, the overall machine parts, structural design and parameter adjustment are also different. The control system is only one of them. Engine (servo motor), shifting The box (reducer), chassis/suspension (structural parts), etc. have a great influence on the overall performance of the robot.
The national standard "GB/T 12642 - 2001 Industrial Robot Performance Specifications and Test Methods" defines the performance indicators of more than a dozen types of robots, of which three are often mentioned: repeated positioning accuracy, pose accuracy, and trajectory accuracy.
In general, the performance of an industrial robot control system can be indirectly represented by the pose accuracy and trajectory accuracy of the robot.
1. Pose Accuracy:
The pose accuracy of a robot generally refers to pose repetition.
The pose of the robot refers to the pose of the robot relative to a certain reference coordinate system. The repeat pose accuracy is one of the most important technical indicators of the robot. The index reflects the electromechanical performance and the use effect of the robot, that is, the robot is the same. The command pose is repeated from the same direction for n times and then the position of the pose is consistent. Generally, a laser tracker is used to measure the position and accuracy, as shown in the following figure:
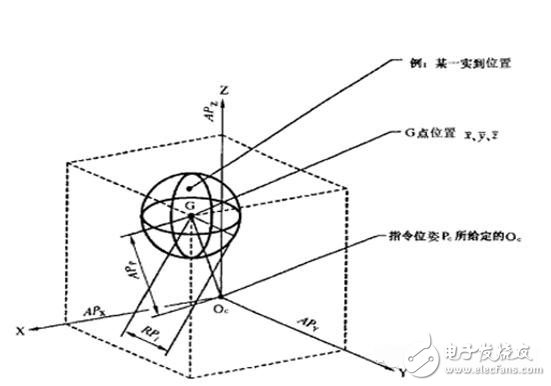
To achieve high pose accuracy, the control system needs to provide the following features:
Compensating for kinematic parameter errors of mechanical linkages, such as link machining errors, assembly errors, mechanical tolerances, etc.
Compensate for joint flexibility and link flexibility;
Provides high precision mechanical zero calibration.
2, track accuracy (Path Accuracy):
The trajectory accuracy of the robot generally refers to the trajectory repeat accuracy, which indicates the degree of consistency of the trajectory when the robot repeats n times for the same trajectory command. Generally, the laser tracker is used for testing, and the robot repeatedly takes a certain track n times, and then takes the radius of the cross section of the track bar composed of n tracks. As shown below:
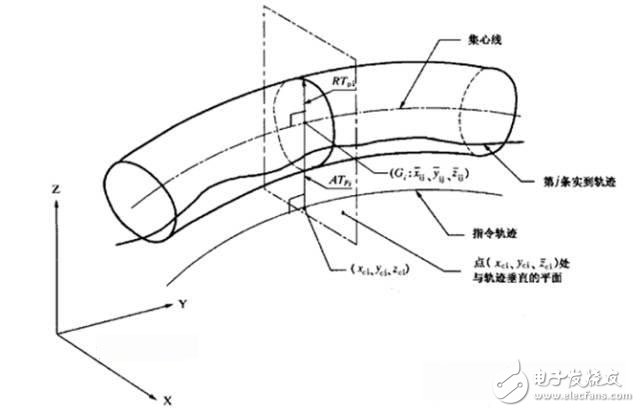
Model Based Control is generally used to improve trajectory accuracy. ABB's comparison of its Quick Move and True Move demonstrates the use of model control to ensure that the robot maintains very high track consistency at any speed the system allows.
In addition, in order to achieve high trajectory accuracy, joint friction compensation for the robot is also necessary.
Trench Cover,Trench Drain,Drain Cover,Steel Trench Covers
Hunan Furui Mechanical and Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd. , https://www.thresher.nl