Here are some of my knowledge of FPGA power estimation and how to design for low power:
Power analysis
The total power consumption of the entire FPGA design consists of three parts of power: 1. Chip static power; 2. Design static power; 3. Design dynamic power.
Chip static power consumption: The power consumed by the leakage current of the transistor when the FPGA is not configured after power-on.
Design static power: When the FPGA configuration is complete, when the design has not started, you need to maintain the I / O quiescent current, clock management and static power consumption of other parts of the circuit
Design dynamic power consumption: the power consumption of the design after the normal startup of the FPGA design; this part of the power consumption depends mainly on the level used by the chip, and the internal logic and routing resources of the FPGA.
Obviously, the power consumption of the first two parts depends on the FPGA chip and the hardware design itself, and it is difficult to make a big improvement. It can be optimized for Part 3 power consumption: design dynamic power consumption, and this part of the power consumption accounts for about 90% of the total power consumption, so reducing the design dynamic power consumption is a key factor to reduce the power consumption of the entire system. It is also mentioned above that the power consumption will increase the heat of the FPGA. Is there a quantitative analysis? The answer of course is yes, as follows:
Tjmax > θJA * PD + TA
Where Tjmax represents the maximum junction temperature of the FPGA chip (maximum juncTIon temperature); θJA represents the junction thermal impedance of the FPGA and the surrounding atmosphere (JuncTIon to ambient thermal resistance), the unit is °C/W; PD represents the total power consumption of the FPGA (power dissipaTIon), the unit is W; TA represents the ambient temperature.
Take the XC7K410T-2FFG900I series chip as an example, θJA = 8.2 °C/W. In the environment of TA = 55 °C, if the junction temperature Tjmax does not exceed 100 °C, the total power consumption of the FPGA can be estimated: PD <(Tjmax – TA)/θJA=(100 - 55)/8.2=5.488W, the previously estimated 20W is too far apart, so optimization is essential:
1) Decrease θJA: The thermal impedance depends on the thermal conduction efficiency of the chip and the environment. The thermal impedance can be reduced by adding a heat sink or a fan.

figure 1
2) Reduce PD: By optimizing the FPGA design and reducing the total power consumption, this is also the focus of this article.
2. Power estimation
Before explaining the low-power design, introduce the Xilinx Power Estimation Tool XPE (Xilinx Power EsTImator). The XPE is mainly used in the early stage of the project, in the system design, and the RTL code is not used in the stage of power estimation. It is based on The tools of EXCEL, as shown in Figure 2, are very rich in features.
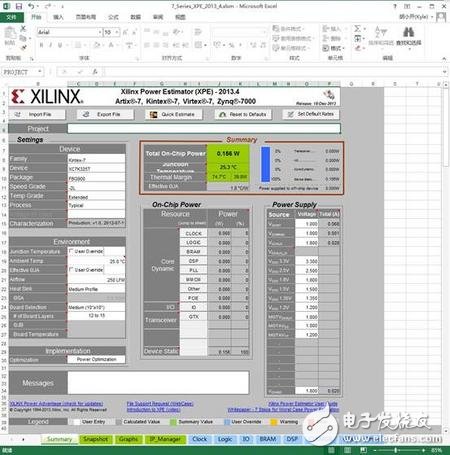
figure 2
After the design is fully implemented, you can use vivado's own power analysis tool to accurately calculate power consumption. Open the design after the integrated implementation, click on report power to get the results of the power analysis, as shown in Figures 3 and 4.
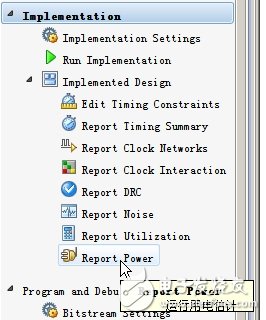
image 3
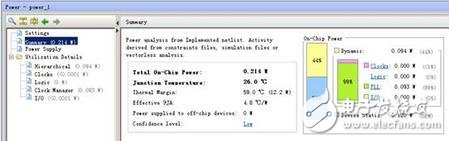
Figure 4
Y10T Isotropic Ferrite Magnet,Anisotropic Ferrite Magnet y35, Motor Rotor Ferrite Magnet
HU NAN YUBANG MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO.,LTD , https://www.ybmagnet.com