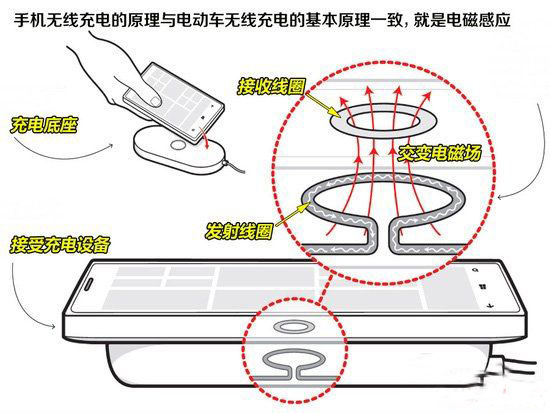
Inductive wireless energy transmission is a relatively mature technology. Many mobile phones are wirelessly charged, and even our common induction cooker is the principle. Since the space of the digital device is small, the receiving coil is small, and the power of the charging device is small, the charging distance is usually close (even if it needs to be in contact with the charging stand), but the relative electromagnetic radiation is also small. A: There are many types of wireless charging, such as inductive, resonant, microwave, etc., but in general, their basic principles are the same, that is, using electromagnetic induction of alternating electromagnetic fields to achieve Wireless transmission of energy.
This article refers to the address: http://
Resonance is a type of charging technology currently being developed by MIT. It is not complicated to say. They use the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction and the principle of resonance to improve the efficiency of wireless charging. The distance of resonance transmission is farther than that of ordinary induction, and MIT is currently conducting research on miniaturization - the technical pressure on this is not too great for electric vehicles with a few meters.
Microwave transmission has appeared more in science fiction movies or novels. In fact, it is also a good way to transmit wireless power. It is limited by the transmission power and is not used on a large scale. The biggest advantage of microwave transmission is that the transmission distance is far, and even the energy transmission between the spacecraft and the ground can be realized. At the same time, directional transmission can be realized (the transmitting antenna has directionality), and the future prospect is worth looking forward to.
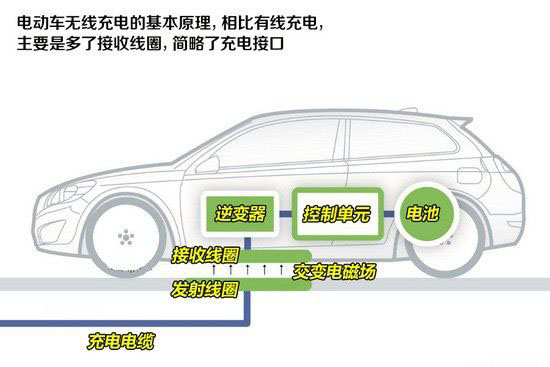
A: The first benefit of wireless charging is that you don't need a line, and you don't have to worry about finding a charging line everywhere. The second is that the standard for wireless charging in terms of hardware is easier to unify.
What are the benefits of wireless charging? What are the issues to be solved?
A: First, transmission efficiency is a problem faced by all wireless charging. This is especially true for "electric appliances" that charge more power such as electric vehicles. First, electric energy is converted into radio waves, which are then converted into electric energy by radio waves. Both conversions will lose a lot of energy.
Second, electromagnetic compatibility is also one of the technical bottlenecks that wireless charging needs to solve. Electromagnetic waves are prone to leaks. When high-powered wireless charging devices are used, they can also affect surrounding biological and electronic devices, and even endanger human health. Installing a wireless charging device with a closed, automated smart garage is a good way to solve electromagnetic compatibility, but the cost is also very high.
Third, electrical standards and other aspects.
What are the typical cases?
A: From the perspective of foreign car companies, traditional cars such as Tesla Volvo Audi and Mercedes-Benz have begun to develop or test the wireless charging system of their electric vehicles. The global communications and the newcomers in the IT industry have also extended their "tentacles" to new areas of wireless charging for electric vehicles. In the planning of wireless charging and the choice of static or dynamic charging, domestic and foreign car companies are different.
First, Volvo: use the road for wireless charging

Volvo has built a 1/4 mile track at the H llered test center in Sweden and tested it with a truck. In the future, when an electric car needs to be recharged, a wireless transmitter must be installed to make the road aware, and then the charging function is activated by an encrypted signal. Volvo's charging system is suitable for high-speed roads because of the speed requirements. If the future comes true, people don't have to worry about power when they travel far. In Sweden, the Volvo Group, the Swedish power company Alstom, and the Swedish Energy Agency are working together to test the use of roads to charge electric vehicles. By laying two power lines on the road, the electric vehicles can be supplied with electricity. The core of this technology is that the car has to be equipped with a collector, the collector is connected to the cable on the road, and it is charged by DC. The car does not have to be in the center of the cable, but it must be more than 60 kilometers per hour.
The use of road surface for wireless charging is likely to be the future direction of development. Compared with the facilities on the ground, it has the advantage of not requiring floor space and reducing construction and maintenance costs. Cars don't need to stop for charging and drive safely.
Volvo's move is to create a good charging network for electric vehicles. However, it needs to face many popular issues, such as road construction, design issues, collectors, and electric vehicle support. Just like driverlessness, this is a huge project that is difficult to achieve in the short term.
Qualcomm: Halo's Inductive Charging System
Qualcomm Halo's inductive charging system is a relatively straightforward idea: a transformer consisting of two ferrites, each with a wire coil next to it. In general, the two parts are connected together. The alternating current is converted into a magnetic field in the first coil and then converted to direct current by the second coil. Qualcomm Halo separates the two ferrites and allows the system to achieve maximum power transfer across the air gap. At the Formula E Electric Formula Championship on April 22, 2015, Qualcomm demonstrated its own Halo wireless car charging technology. Just drive the car directly above the charging pad and the current will begin to be delivered to the car when the charging coils are aligned. If there is a foreign object between the car and the mat, the system can also automatically suspend charging.
Halo's wireless charger is placed in the rear of the car, a metal box slightly larger than the set-top box, and connected to several orange wires. As for the other half of the charger, it is just below the car. Inductive charging can actually be applied to moving vehicles. Halo currently has a semi-dynamic charging capability for power transfer at speeds up to 30 mph.
Nissan wireless charging car
The Nissan Rubik's electric vehicle uses an electromagnetic induction that provides power between the power supply coil and the power receiving coil. A power receiving coil device is installed on the chassis of the automobile, and another power feeding coil device is installed on the ground. When the electric vehicle drives to the power supply coil device, the power receiving coil can receive the current of the power feeding coil, thereby charging the battery. . At present, the rated output power of this device is 10kW, and the average electric vehicle can be charged within 7-8 hours.
Japanese wireless plug-in hybrid bus: electromagnetic induction type, the power supply coil is buried in the concrete of the charging stand. After the car is turned on the charging station, when the car coil is aligned with the power supply coil (coincident), an indicator light on the instrument panel inside the car will light up, and the driver presses the charging button to start charging.
ZTE: Wireless power supply system
ZTE's wireless power supply system transmits power through non-contact electromagnetic induction. When the charging vehicle is parked in the charging parking space, it can automatically establish a communication link between the ground system and the vehicle system through wireless access to the communication network of the charging field, and complete vehicle authentication and other related information exchange.
The charging bit can also be interconnected with the cloud service center by wire or wirelessly. In the event of any potential for charging and receiving power, the ground charging unit will immediately stop charging and alert to ensure that the charging process is safe and reliable. Most importantly, the wireless charging system does not work at all while the vehicle is running, even if the vehicle is driving over it or in bad weather such as thunderstorms.
Transfer Switch,Protection Transfer Switch,Adjustment Transfer Switch,Protect Switchgear
zhejiangjinyidianqiyouxiangongsi , https://www.jooeei.com