Today's robots have human-like limb and sensory functions, a certain degree of intelligence, flexible movement procedures, and can be manipulated without human intervention. All of this is indispensable to the sensor's credit. The sensor is an important helper for the robot to perceive the outside world. They are like human perception organs. The robot's visual, force, touch, smell, taste and other perceptions of the external environment are provided by sensors. At the same time, the sensor can also be used to detect the working state of the robot itself, and the robot intelligently detects the external working environment and the object state. And a device that can be converted into an available output signal according to a certain rule. In order to make the robot achieve the highest possible sensitivity, a variety of sensors are installed in its body structure, so how many kinds of sensors should the robot have? Can you be as sensitive as possible as human beings?
The robot sensor can be divided into an internal sensor and an external sensor depending on the object to be detected.
The internal sensor is mainly used to detect the internal conditions of the robot, such as the position, speed, acceleration temperature, motor speed, motor load, battery voltage, etc. of the joints, and send the measured information as feedback information to the controller to form Closed-loop control.
The external sensor is used to obtain information about the robot's working object and the external environment. It is an information channel for the robot to interact with the surrounding, and is used to perform sensors such as vision, proximity, touch, and force, such as distance measurement and sound. , light, etc.
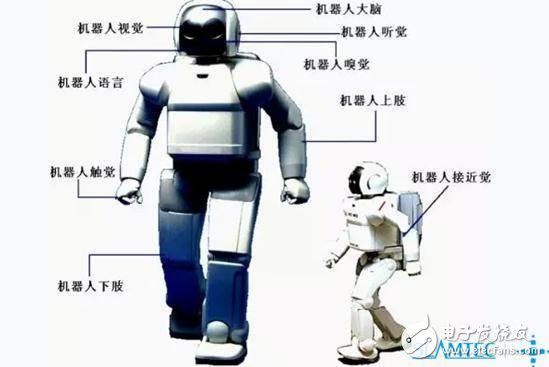
The details are as follows:
1, visual sensor
Machine vision is a system that enables robots to have a perceptual function. It acquires images through visual sensors for analysis, allowing robots to recognize objects, measure and judge, and achieve positioning and other functions. According to industry sources, the smart smart sensors currently used in China account for about 60% of the market share of the machine vision system market. The advantage of the visual sensor is that the detection range is wide and the information is rich. In practical applications, multiple visual sensors are often used or used together with other sensors. The shape, distance, speed and other information of the object can be obtained by a certain algorithm.
The depth of camera-based computing vision has become one of the hottest investment and entrepreneurial hot spots in the high-tech industry. Interestingly, many of the cutting-edge results in this field were first introduced by startups and then acquired by giants. For example, Intel acquired the RealSense camera, Apple acquired Kinect's technology provider PrimeSense, and Oculus acquired a high-accuracy target. Israeli technology company Pebbles Interfaces for gesture recognition technology. Although the entrepreneurial team in the field of computing in China has not yet entered the mainstream of investors on a large scale, the best among them has already achieved remarkable results.
In-depth cameras were introduced by IBM in the 1980s. This super company, which holds almost all of the hard drive's underlying data in the past, present and future, is the leader of the times. PrimeSense, founded in Israel in 2005, is a pioneer in the commercialization of this technology. At that time, the depth camera in the consumer market was still in the concept stage. Previously, the depth camera was only used in the industrial field to provide graphic vision services for robotic arms and industrial robots. Microsoft Kinect, which provides technical solutions, has become the pioneer of deep camera in the consumer field and has driven the entire industry to develop the technology for civilian use.
2, acoustic sensor
The sound sensor acts like a microphone (microphone). It is used to receive sound waves and display a vibrating image of the sound. However, the intensity of the noise cannot be measured. Acoustic sensors are primarily used to sense and interpret sound waves in a gas (non-contact sensation), liquid or solid (contact sensation). The sonic sensor complexity can range from simple sound wave detection to complex acoustic frequency analysis until individual speech and vocabulary recognition in continuous natural language.

It is reported that since the 1950s, BELL Labs has developed the world's first speech recognition Audry system, which can recognize 10 English numbers. By the 1970s, voice recognition technology was rapidly developed. Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm, vector quantization (VQ) and Hidden Markov Model (HMM) theory were successively proposed to realize the isolated voice of specific people based on DTW technology. recognition system. In recent years, voice recognition technology has moved from the laboratory to practical, and many companies at home and abroad have developed corresponding products using voice recognition technology. More well-known companies include Spirit, Keda Xunfei, and giants such as Tencent and Baidu, all of which are in the field of voice technology.
3, distance sensor
The distance sensors for intelligent mobile robots include laser range finder (and measurable angle), sonar sensor, etc. The laser radar sensor developed in recent years is currently a mainstream type, which can be used for robot navigation and avoiding obstacles. For example, the RPLIDAR A2 laser radar developed by SLAMTEC can perform 360-degree full-scale scanning ranging to obtain the contour map of the surrounding environment. The sampling frequency is up to 4000 times per second, which is the highest measurement frequency of the low-cost laser radar in the industry. The SLAMWARE autonomous positioning navigation solution with SLAMTEC can help robots build their own maps, real-time road planning and automatically avoid obstacles.
4, touch sensor
Tactile sensors are primarily used in sensors that mimic haptic functions in robots. Tactile sensation is an important sensory function when people are in direct contact with the external environment. Developing a tactile sensor that meets the requirements is one of the key technologies in the development of robots. With the development of microelectronics technology and the emergence of various organic materials, a variety of tactile sensor development solutions have been proposed, but most of them are currently in the laboratory stage, and there are not many products.

5, proximity sensor
The proximity sensor is interposed between the tactile sensor and the visual sensor to measure distance and orientation, and can blend information from the visual and tactile sensors. The proximity sensor can assist the function of the vision system to determine the orientation and shape of the object while identifying its surface shape. Therefore, in order to accurately grasp the components, the accuracy requirements of the robot proximity sensor are very high. This type of sensor has the following main functions:
Find obstacles in front and limit the range of motion of the robot to avoid collisions with obstacles.
Obtain the necessary information before touching the object, such as the relative distance from the object, the relative inclination, in order to prepare for the subsequent action. The distance between points on the surface of the object is obtained, thereby obtaining information about the surface shape of the object.
6, sliding sensor
The sliding sensor is mainly a sensor for detecting the degree of slip between the robot and the gripping object. In order to determine an appropriate grip force value when grasping an object, it is necessary to detect the relative sliding of the contact surface in real time, and then judge the grip force, gradually increasing the force without damaging the object, and the sliding detection function is necessary for realizing the flexible grip of the robot. condition. The recognition function can be realized by the sliding sensor, and the surface roughness and hardness of the object to be grasped can be judged. The sliding sensor can be divided into three categories according to the sliding direction of the measured object: non-directional, unidirectional and omnidirectional sensors. The non-directional sensor can only detect whether there is slippage and can not distinguish the direction; the unidirectional sensor can only detect the slip in a single direction; the omnidirectional sensor can detect the sliding in the direction. Such sensors are typically made in a spherical shape to meet the needs.
7, force sensor
The force sensor is a sensor for detecting the interaction force between the robot's own force and the external environmental force. Force sensors are often placed at the joints of the robot to measure the force indirectly by detecting the deformation of the elastomer. The force sensor installed at the joint of the robot often appears in a fixed three-coordinate shape, which is beneficial to meet the requirements of the control system. The current six-dimensional force sensor can measure the full force information, because it is mainly installed in the wrist joint and is called the wrist force sensor. Most of the wrist force sensor adopts the principle of strain electric measurement. According to its elastic structure, it can be divided into two types, the barrel type and the cross type wrist force sensor. Among them, the tubular type has the characteristics of simple structure, high utilization rate of elastic beam and high sensitivity; and the cross-shaped sensor has simple structure and easy coordinate establishment, but high processing precision.
8, speed and acceleration sensor
Speed ​​sensors measure both translational and rotational motion speeds, but in most cases are limited to measuring rotational speed. Using the derivative of the displacement, especially the photoelectric method, the light is irradiated to the rotating disk, the rotation frequency and the number of pulses are detected, the rotation angle is determined, and a gap is formed by the disk, and the angular velocity is recognized by the two photodiodes, that is, the rotation speed This is the photoelectric pulse speed sensor.
An acceleration sensor is a sensor that measures acceleration. It usually consists of mass, damper, elastic element, sensitive component and adaptive circuit. During the acceleration process, the sensor obtains the acceleration value by using Newton's second law by measuring the inertial force of the mass. Depending on the sensor's sensitive components, common accelerometers include capacitive, inductive, strain, piezoresistive, and piezoelectric.
For robots to be as sensitive as humans, the eight sensors of vision sensors, acoustic sensors, distance sensors, tactile sensors, proximity sensors, force sensors, sliding sensors, speed and acceleration sensors are extremely important to robots, especially It is essential that the robot's five sensory sensors are essential. From the anthropomorphic function, vision, force and touch are the most important. It has entered the practical stage, but its senses, such as hearing, smell, taste, and slid. The sensor is still waiting for one to overcome.
Outdoor Emergency Portable Power Station
Langrui Energy (Shenzhen) Co.,Ltd , https://www.langruienergy.com