Network cable, the most inconspicuous part of the computer network, the most easily overlooked parts. However, with the expansion of the network scale and the increasing demand for network cables, the importance of network cables is becoming more and more obvious. Let's take a look at the basics of the next network cable.
Twisted pairs are commonly found in Category 3, Category 5 and Category 5, Category 6 and the latest Category 7 lines. The former has a thin wire diameter and the latter has a coarse wire diameter. The model number is as follows:
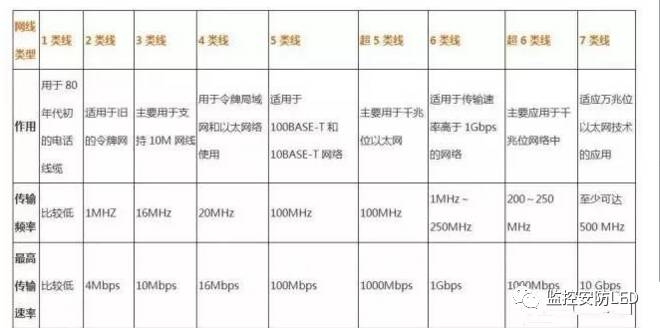
One type of line: mainly used for transmitting voice (one type of standard is mainly used for telephone cables before the early 1980s), unlike data transmission.
Class 2 line: The transmission frequency is 1 MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 4 Mbps. It is commonly used in the old token network using the 4 MBPS specification token transfer protocol.
Category 3: A cable specified in the ANSI and EIA/TIA568 standards. The cable has a transmission frequency of 16 MHz and is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 10 Mbps, mainly for 10BASE--T.
Category 4 cable: This type of cable has a transmission frequency of 20MHz and is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 16Mbps. It is mainly used for token-based LAN and 10BASE-T/100BASE-T.

Category 5 cable: This type of cable increases the winding density, and is a high-quality insulating material with a transmission rate of 100MHz. It is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps. It is mainly used for 100BASE-T and 10BASE- T network. This is the most commonly used Ethernet cables.
Super Category 5: Super Category 5 has low attenuation, low crosstalk, and higher attenuation and crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (Structural Return Loss), smaller delay error, and greatly improved performance. The Super Category 5 cable is mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps).
Category 6 line: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz ~ 250MHz. The Category 6 wiring system should have a large margin in the integrated attenuation crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) at 200MHz, which provides twice the bandwidth of the Super Category 5. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than the Category 5 standard and is best suited for applications with transmission rates above 1Gbps.
An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5 is that it improves performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss. For a new generation of full-duplex high-speed network applications, excellent return loss performance is extremely important. The basic link model is eliminated in the six categories of standards. The cabling standard adopts a star topology. The required cabling distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90 m, and the channel length cannot exceed 100 m.
Super Category 6 line: Super Category 6 line is an improved version of Category 6 line. It is also an unshielded twisted pair cable specified in ANSI/EIA/TIA-568B.2 and ISO Class 6/E standard. Main application In a gigabit network. In terms of transmission frequency, like the Category 6 line, it is also 200-250 MHz, and the maximum transmission speed can reach 1 000 Mbps, but it has a great improvement in crosstalk, attenuation and signal-to-noise ratio.

Category 7 line: This line is the latest twisted pair in the ISO 7/F standard. It is mainly used to adapt to the application and development of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology. But it is no longer an unshielded twisted pair, but a shielded twisted pair, so its transmission frequency is at least 500 MHz, which is more than twice that of Category 6 and Super Category 6 transmission rates. Up to 10 Gbps.
Twisted pair can be divided into unshielded twisted pair (UTP=UNSHIELDED TWISTED PAIR) and shielded twisted pair (STP=SHIELDED TWISTEDPAIR). The outer layer of the shielded twisted pair cable is wrapped with aluminum and platinum to reduce radiation, but it does not completely eliminate the radiation. The shielded twisted pair is relatively expensive and difficult to install than the unshielded twisted pair cable.
Unshielded twisted pair cable has the following advantages: unshielded jacket, small diameter, saving space occupied; light weight, easy to bend, easy to install; minimize or eliminate near-end crosstalk; flame retardant; Sex and flexibility for structured cabling.
There are some draft products here, which will not be displayed on the website. These products can be modified later to enrich the content of the website. If you want to know more about our company, you can go to our website to check, there will be what you want, or you can consult us. Nice to meet you and looking forward to our cooperation.
Draft-waiting For Releasing,Draft-waiting For Releasing,Draft-waiting For Releasing
ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.wireharnessetop.com